Domino makes it easy to deploy your model to a REST endpoint using Model APIs. Domino streamlines deployment so you can start making calls to your Model API REST endpoints to get predictions from your models quickly. Learn how to:
-
Deploy a model for synchronous inference (real-time).
-
Access Domino assets in a model image.
-
Request predictions from a Model API endpoint.
-
Retrain a model.
When you deploy a Model API, Domino packages the project’s files as a Flask application. By default, Domino copies all project files into the model image including the compute environment, project files, a Flask/Plumber harness that exposes the REST interface, and an authentication and load balancing layer.
A Domino Model API is a REST API endpoint wrapped around your inference code. You supply the arguments to your inference code as parameters in the REST request payload, the response from the API includes the prediction. When a Model API is published, Domino runs the script that contains the function. As the process waits for input, any objects or functions from the script remain in memory. Each call to the endpoint runs the function. Since the script is only sourced at publish time, expensive initialization processes occur only once rather than on each call.
Domino supports a few different methods for model deployment:
-
Deploy from the UI - For quick, one time deployments.
-
Deploy with a scheduled job - Schedule a job and deploy a model from the job. Especially useful for keeping models trained on the latest data on a regular cadence.
-
Deploy with the API - Use the Domino API to schedule jobs from other applications.
Deploy from the UI
Use the Domino UI to deploy your model directly from your browser.
-
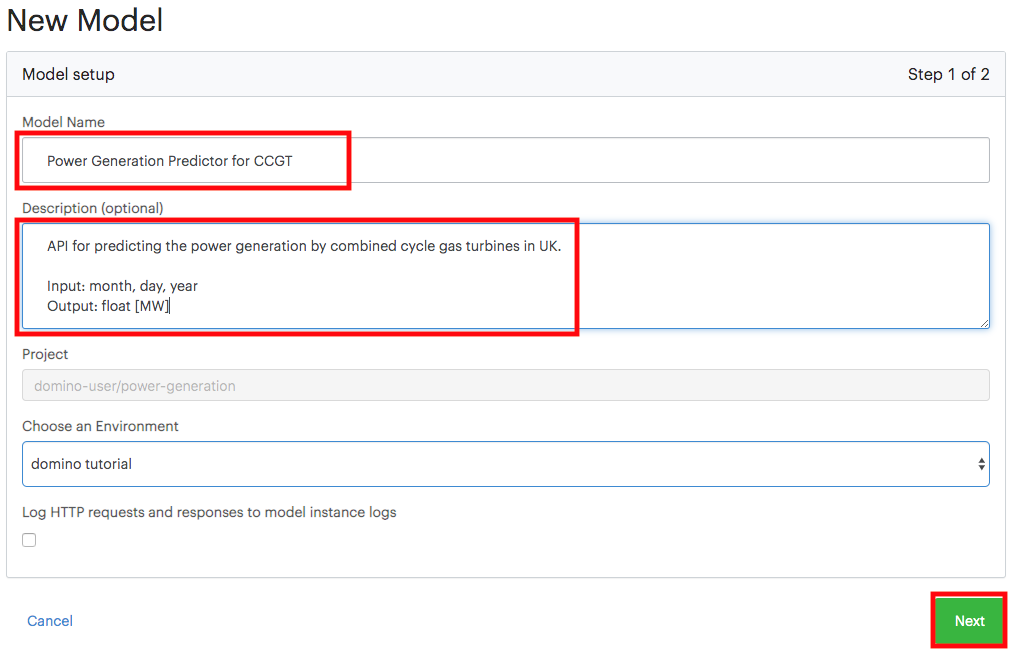
In your project, go to Model APIs > Create Model API.
-
Provide a name, description, and select the prediction code that executes when the model is called.
-
(Optional) Select a custom compute environment to build the deployed model container.
-
(Optional) Configure scaling. The number of instances and compute resources attached to each instance. See Scale model deploymentsfor more information.
Deploy with a scheduled Job
You can use scheduled jobs to deploy models. This is especially useful for keeping models trained on the latest data. Select the Model API from the Update Model API menu when scheduling a job. This setting uses the state of the project’s files after the run to build and deploy a new Model API.
You can use automated deploy jobs to automatically keep your Model API up-to-date by using a training script in the job that trains on fresh data.
Deploy with the Domino API
Use Domino’s APIS to programmatically build and deploy models. For more information, see the API docs.
Users may prefer to host their models in a separate cluster or data plane than where the model was built, either for scalability or data proximity reasons. Domino facilitates this through its Create Model API feature, allowing models to be packaged and deployed close to where they’ll have the most impact.
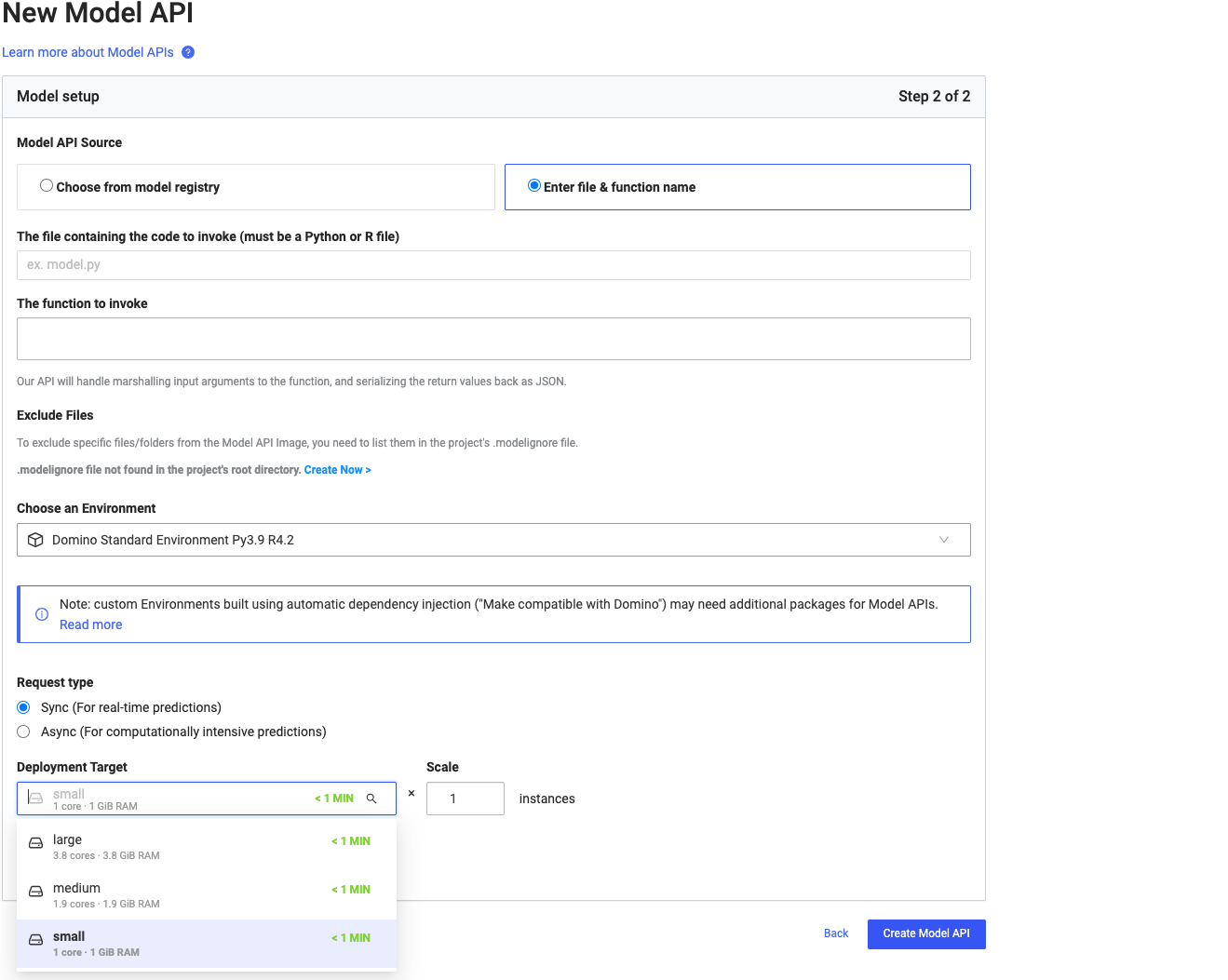
Starting from version 5.9, Model APIs now support hardware tiers instead of Resource Quotas. When deploying Model APIs to a remote data plane, select the hardware tier associated with the desired local or remote data plane from the Deployment Target list (previously resource quotas) in the Model API Create UI.
Domino containerizes the model (MLflow or Project) as a Model API image, deploys it against an endpoint, and exposes a URL local to that remote cluster where a Nexus data plane has been deployed. Users can invoke it via the exposed URL and data movement is restricted to this remote data plane only.
Limitations: Currently, Model APIs deployed to a remote data plane do not support the asynchronous requests (described below) and integrated model monitoring.
You can still access Domino artifacts from model images. However, there are nuances to each artifact type. Learn how to use Domino artifacts from your model image and keep them up to date.
Model API environments
When you deploy a Model API, select the compute environment to include in the model image. The environment bundles packages required by the inference script execution ahead of time.
-
Model API hosts don’t read
requirements.txtfiles or execute commands defined in the pre-setup, post-setup, pre-run, or post-run scripts of your environment. If your project usesrequirements.txtor any setup scripts to install specific packages or repositories, add them to the Dockerfile instructions of your environment. -
Your Model API doesn’t inherit environment variables set at the project level. However, you can set Model API-specific environment variables on the Model settings page. This separation decouples the management of projects and deployed models. See Secure Credential Storage for more details.
Model API project files
Your Model API can access files from the project. Domino loads the project files onto the Model API host, similar to a Run or Workspace executor host, with a few important differences:
-
Domino adds project files to the image when you build a Model API. Starting or stopping the Model API won’t change the files on the model host. To update the model host files, you need to create a new version.
-
Domino pulls Git repositories attached to projects when you build a Model API. Starting or stopping the Model API won’t change the files on the model host. To update the model host files, you need to create a new version.
-
The Model API host mounts project files at
/mnt/<username>/<project_name>. This location differs from the default location for Runs or Workspaces,/mnt/. You can use the Domino environment variableDOMINO_WORKING_DIRto reference the directory where your project is mounted. -
The Model API image excludes project files listed in the
.modelignorefile that are located in the project’s root directory. Excluded files are not mounted to the Model API host.
Add a Kubernetes volume to a synchronous Model API container
When you load inference data or write the response to an external volume, you can add Kubernetes volumes:
-
Select a Model API from the Model APIs page.
-
Go to Settings > Advanced > Add Volume.
NoteOnly hostPaths are supported. -
Enter the values required.
-
Name - Kubernetes volume name
-
Mount Path - mount point it the Model API container
-
path - the path of the Kubernetes host node that must be mounted in the Model API containre, as configured by your administrator
-
Read Only? - the read/write permission of the mounted volume
-
See the Kubernetes documentation for more details.
After you deploy the Model API, and its status changes to Running, try test inputs with the Tester tab in the Model API UI.
|
Tip
| Use the Request window to make calls to the Model API from the Domino web application. You will find additional tabs with code samples to call the Model API with other tools and in various programming languages. |
JSON requests
Send your requests as JSON objects. Depending on how you wrote your prediction script, you need to format the JSON request as follows:
-
If you use named parameters in your function definition, use a dictionary or parameter array in your JSON request. For example,
my_function(x, y, z), use{"data": {"x": 1, "y": 2, "z": 3}}or{"parameters": [1, 2, 3]}. -
If you use a dictionary in your function definition, use only a parameter array. For example,
my_function(dict)and your function then usesdict["x"],dict["y"]. Send the request:{"parameters": [{"x": 1, "y": 2, "z": 3}]}. -
In Python, you can also use kwargs to pass in a variable number of arguments. If you do this:
my_function(x, **kwargs)and your function then useskwargs["y"]andkwargs["z"], you can use a data dictionary to call your model API:{"data": {"x": 1, "y": 2, "z": 3}}.
Domino converts JSON data types to the following R and Python data types.
| JSON Type | Python Type | R Type |
|---|---|---|
dictionary | dictionary | named list |
array | list | list |
string | str | character |
number (int) | int | integer |
number (real) | float | numeric |
true | True | TRUE |
false | False | FALSE |
null | None | N/A |
The model API’s returns the result object, which is a literal, array, or dictionary.
Synchronous requests
-
Request a prediction and retrieve the result: Pass the URL of the Domino Model API, authorization token, and input parameters. The response object contains the status, response headers, and result.
response = requests.post("{DOMINO_URL}/models/{MODEL_ID}/latest/model", auth=("{MODEL_ACCESS_TOKEN}", "{MODEL_ACCESS_TOKEN}"), json={"data": {"start": 1, "stop": 100}} ) print(response.status_code) print(response.headers) print(response.json())
- Deploy a new version
-
After you retrain your model with new data or switch to a different machine learning algorithm, publish a new version of the Model API. To follow best practices, stop a previous version of the Model API and then deploy a new version.
Use spot instances for Model APIs (PREVIEW)
We support serving Model APIs using cost effective Spot instances. Select hardware tier that uses node pool using Spot instances.
If AWS interrupts a spot instance, model APIs deployed on that instance will be affected and either stop responding, if there are no remaining replicas of the model API on other AWS instances, or the remaining replicas still running on unaffected instances will experience an increased load and may have their performance degraded or also stop working, depending on the runtime characteristics of each model. If this happens, and until AWS spot instances of the requested type become available again, the remediation is to change the hardware tier of the model API to use a non-spot node pool.