Data scientists can publish interactive apps to share their findings with stakeholders. Apps are endlessly flexible and can do things like share results with stakeholders, host interactive analytical dashboards, provide an interface to deployed models, and much more.
Domino supports building apps with your preferred app framework including popular frameworks like Dash, Flask , Streamlit , and Shiny.
But like the rest of Domino, app publishing is open and flexible: you can publish apps using any HTTP framework.
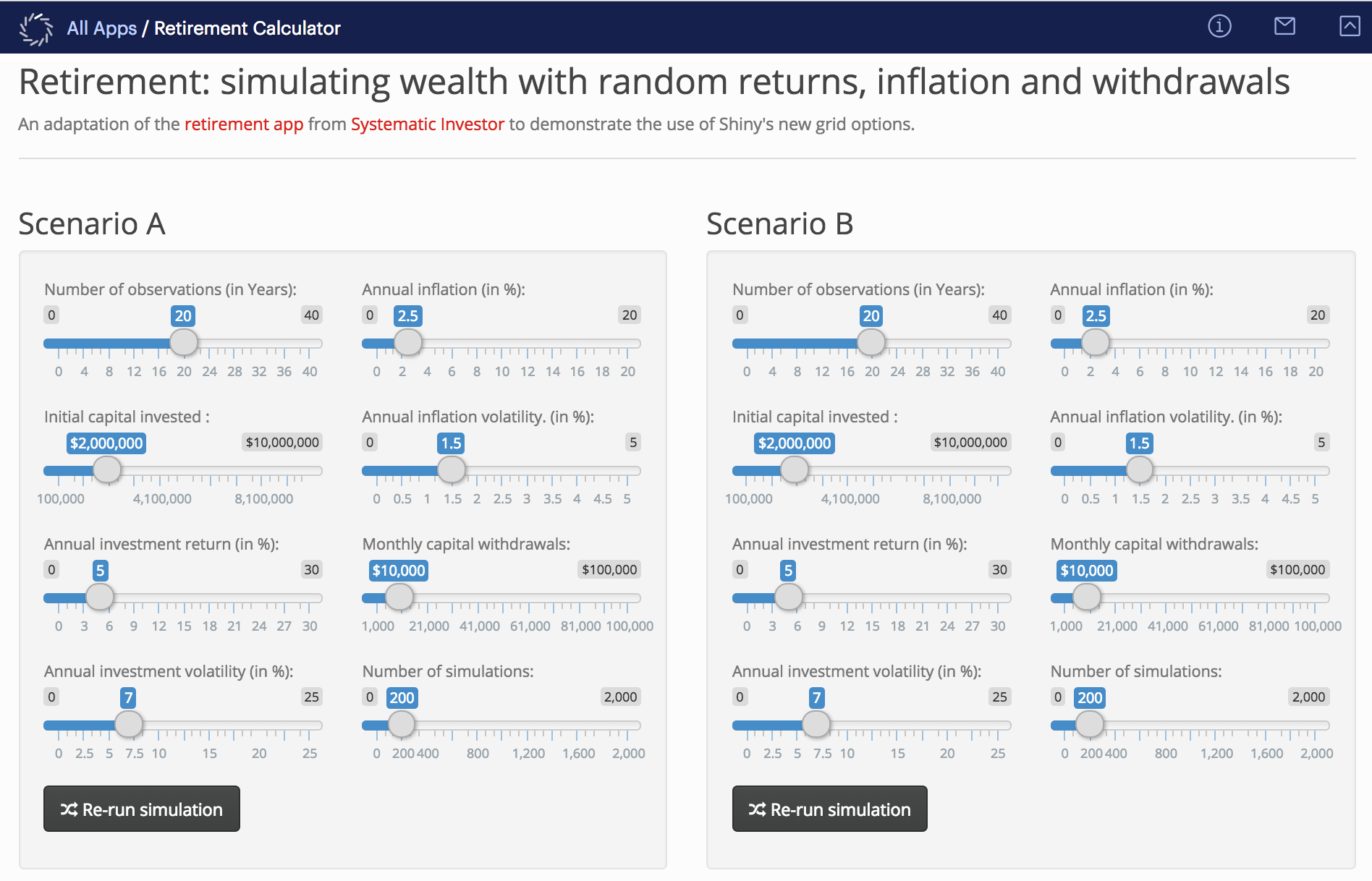
Apps can use Spot instances to save the infrastructure costs.
If AWS interrupts a spot instance, the Apps may fail to load. If this happens, and until AWS spot instances of the requested type become available again, the remediation is to change the hardware tier of the job to use a non-spot node pool.
Secure your apps with permissioning to control access.
View app logs to see who is using your app.
Use version control to snapshot fully reproducible artifacts each time you publish a new version of your app.
Optimize your applications for performance and scale depending on your framework.
For better scale or data location, users might prefer deploying Apps in a separate cluster or data plane than where the model was created. Domino supports this through the Publish Apps workflow, allowing Apps to be deployed where they generate the most value. When publishing an App, choose the hardware tier for the preferred local or remote data plane.