This topic describes how to connect to a Microsoft SQL Server (MSSQL) from Domino. You must have network connectivity between Impala and your Domino deployment.
The easiest way to connect to MSSQL from Domino is to create a Domino Data Source as described below.
-
From the navigation pane, click Data.
-
Click Create a Data Source.
-
In the New Data Source window, from Select Data Store, select SQL Server.
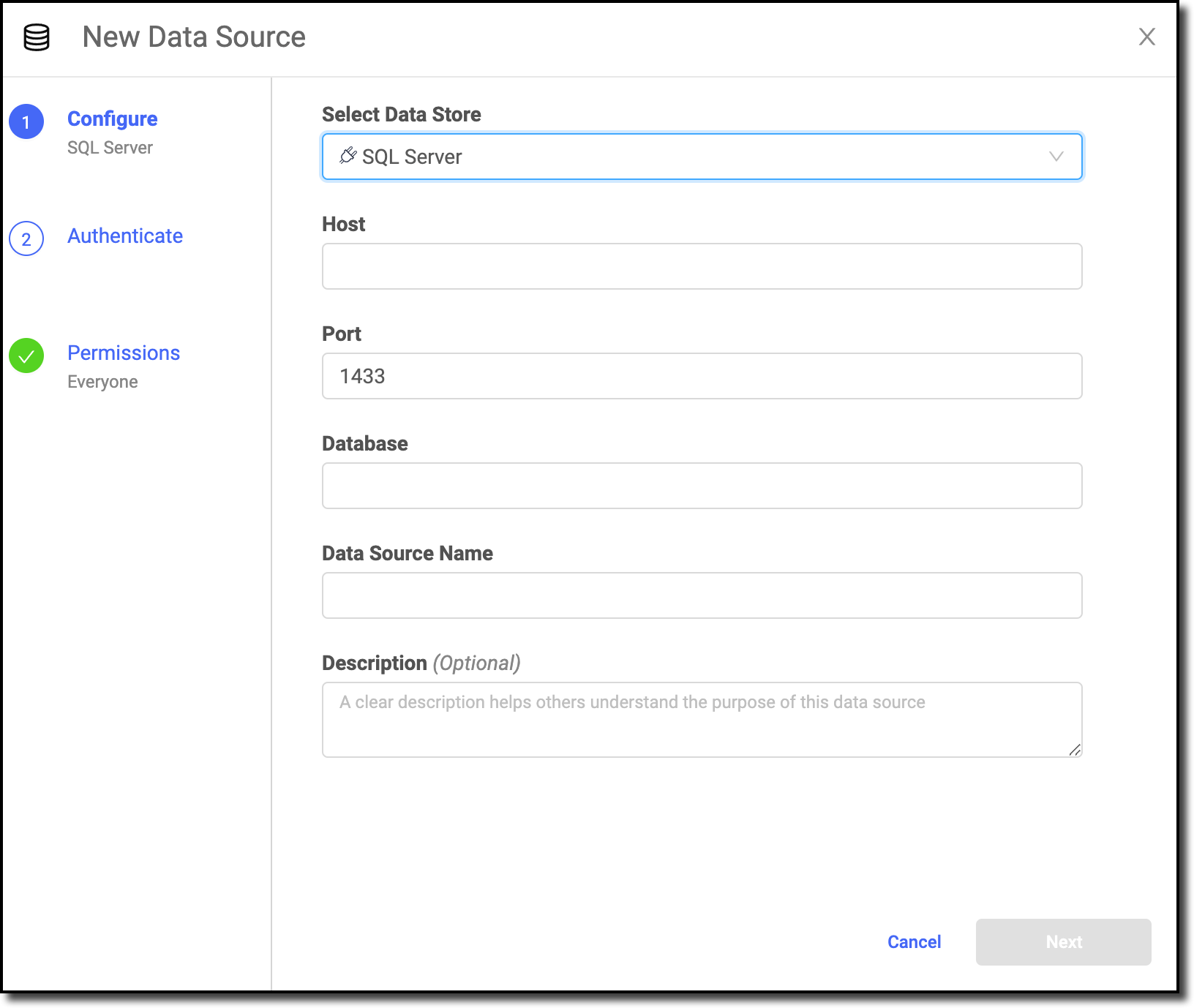
-
Enter the Host. Valid values are
<host string>:3306or<host string>. -
Enter the Port.
-
Enter the name of the Database.
-
Enter the Data Source Name.
-
Optional: Enter a Description to explain the purpose of the Data Source to others.
-
Click Next.
-
Enter the Username and Password to connect to SQL Server. The Domino secret store backed by HashiCorp Vault securely stores the credentials.
-
Click Test Credentials.
-
If the Data Source authenticates, click Next.
-
Select who can view and use the Data Source in projects.
-
Click Finish Setup.
|
Warning
| This section describes an alternate method to connect to the MSSQL Data Source. Domino does not officially support this method. |
-
To interact with MSSQL databases from Python, Domino recommends the pymssql package.
-
Use the following Dockerfile instruction to install pymssql in your environment.
This instruction assumes you already have pip installed.
USER root RUN pip install pymssql USER ubuntu -
You must set up the following Domino environment variables to store secure information about your MSSQL connection.
-
DB_SERVER -
DB_USERNAME -
DB_PASSWORDSee Secure Credential Storage to learn more about Domino environment variables.
See the pymssql documentation for detailed information about how to use the package. The following is an example of connecting to MSSQL with Python where the following is true:
-
You have set up environment variables noted previously.
-
The server hosts a database named
myDatawith a table namedaddresses.from os import getenv import pymssql server = getenv("DB_SERVER") user = getenv("DB_USERNAME") password = getenv("DB_PASSWORD") conn = pymssql.connect(server, user, password, "myData") cursor = conn.cursor() cursor.execute('SELECT * FROM addresses') row = cursor.fetchone() while row: print("ID=%d, Name=%s" % (row[0], row[1])) row = cursor.fetchone() conn.close()
-
R and RODBC to MSSQL
-
To interact with MSSQL databases from R, Domino recommends the RODBC library. You can use an alternative package if you’d like.
-
Use the following Dockerfile instructions to add the MSSQL drivers to your Ubuntu 16.04 environment.
USER root RUN curl https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc | apt-key add - RUN curl https://packages.microsoft.com/config/ubuntu/16.04/prod.list > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mssql-release.list RUN apt-get update RUN ACCEPT_EULA=Y apt-get install msodbcsql17 USER ubuntu -
See Microsoft’s documentation for the Dockerfile instructions to add the MSSQL drivers to your Domino-supported Ubuntu environment.
-
See the RStudio RODBC documentation for information about how to use the package.
-
After connecting to your Data Source, learn how to Use Data Sources.
-
Share this Data Source with your collaborators.