Workspace File Access events capture file-level access activity inside Domino Workspaces. Domino tracks these events only for Domino Datasets and NetApp Volumes. Domino records Workspace lifecycle actions as system events.
Domino records these file operations:
-
Read
-
Write
-
Create
-
Delete
-
Rename
Domino monitors file system activity inside active Workspaces and records relevant events.
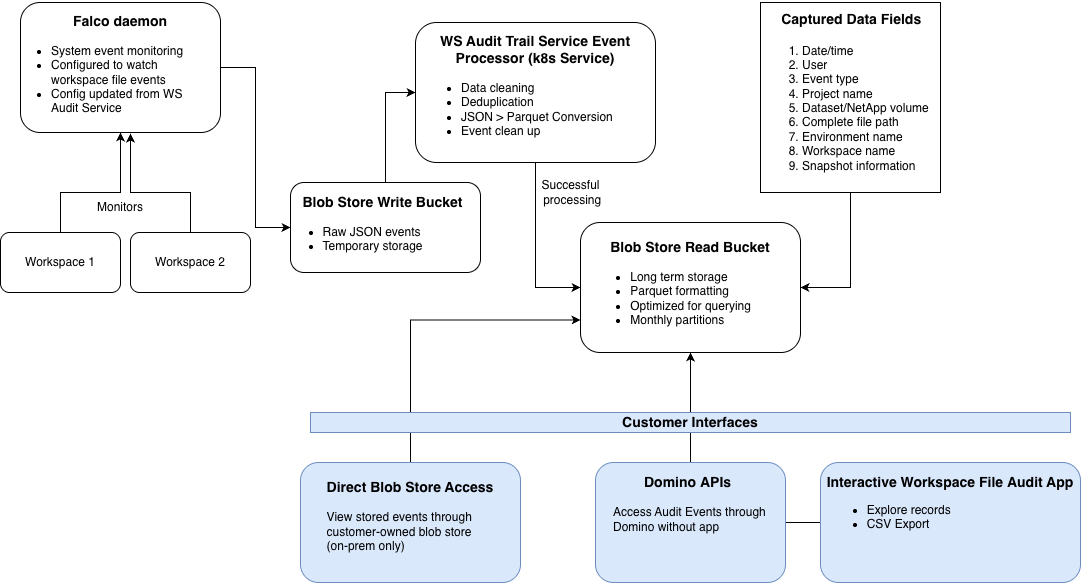
Deduplication
Domino deduplicates events to reduce noise and storage overhead. The system records repeated access to the same file by the same user as a single event. This deduplication uses a configurable time window. The process reduces event volumes while preserving meaningful access records. Advanced configuration has details on how to adjust deduplication settings.
Processing delay
Domino processes events asynchronously in scheduled batches, not in real time. The system captures and stages file system events continuously. It then processes and writes them to object storage during each run (default: every 60 minutes).
Expect a delay between when a file access event occurs and when it appears in object storage, APIs, or the Workspace File Audit App.
You can configure processing frequency with com.cerebro.domino.workspaceFileAudit.eventProcessingInMinutes. The default is 60 minutes (minimum 60, maximum 360).
Storage and retention
Storage location and retention depend on your deployment type:
| Deployment type | Storage location | Who manages | Retention |
|---|---|---|---|
Customer-managed | Customer-owned object storage (S3, Azure Blob, or GCS) | Customer | Customer sets policy |
Domino Cloud | Domino-owned object storage | Domino | 30 years |
Domino Cloud for Life Sciences (DCLS) | Customer-owned S3 | Domino | 30 years |
Performance considerations
Enabling Workspace File Access events adds processing overhead to active workspaces. Based on Domino performance testing, enabling file access auditing typically adds:
-
~ 15 percent CPU usage
-
~ 10 percent memory usage
Workloads with heavy workspace usage or high file I/O may see higher overhead. Plan for larger hardware tiers if you enable this feature.
How hardware sizing is determined
These estimates come from Domino scale and performance testing of the full audit pipeline, including kernel level event capture, event ingestion, and audit record processing. Customers should plan for slightly larger hardware tiers when this feature is enabled.
Monitoring and alerting
|
Important
| Enable Grafana alerting before you enable Workspace File Access auditing. |
Two components are critical for audit data integrity:
-
Falco: Captures file system events
-
Workspace Audit service: Processes and stores events
Monitor for these failure conditions:
-
Falco drops events due to resource pressure
-
Workspace Audit service fails to process events
-
Enable Workspace File Audits: Configure file-level access auditing
-
Advanced configuration of file audit events: Adjust deduplication and processing frequency
-
System events: View and export user and administrative actions
