Linking your GitHub account to Domino allows you to store and manage project code in a GitHub repository. This guide explains how to create a GitHub Personal access token (PAT), add it to Domino, and confirm that the integration works.
Next, you’ll generate a personal access token in GitHub. This token acts as a secure key that Domino will use to talk to your GitHub account.
-
In a separate browser tab, log into GitHub.
-
Click your profile icon in the top-right corner and click Settings.
-
In the left-hand menu, select Developer settings.
-
Select Personal access tokens > Tokens (classic).
-
Click Generate new token > Generate new token (classic).
When you create the token, you’ll decide which permissions it should have. For a quick setup, granting all scopes is easiest. If you prefer, you can limit scopes to just repo and workflow, which are enough for Domino to work properly.
-
Add a brief description in the Note field.
-
Choose an expiry for the token.
-
Select the scopes you want the token to have.
-
Click Generate token.
-
Copy the token and save it in a secure text file on your local machine.
With your token ready, the next step is to tell Domino about it. You’ll add the token as part of your account credentials.
-
Return to Domino.
-
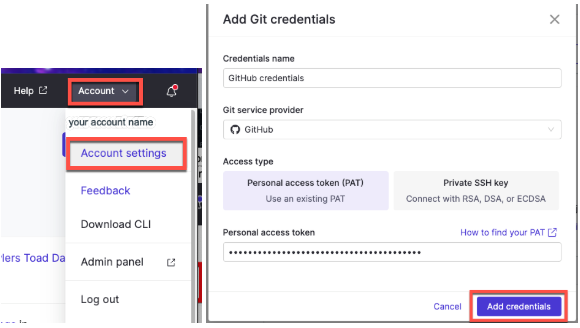
Click Account in the top-right corner and select Account Settings.
-
From the Account Settings panel, select Git Credentials.
-
Click Add Git credentials.
-
Enter the required fields, including the PAT you generated.
-
Click Add credentials.
Your GitHub PAT is now linked to your Domino account.
It’s time to make sure everything works. You’ll do this by creating a test project in Domino and linking it to a newly created GitHub repository.
-
In Domino, go to the Home screen.
-
Click Create Project.
-
Enter a project name, such as
test. -
In the Code section, select Git Service Provider as the code hosting service.
-
From the Service Provider dropdown, select GitHub.
-
Your GitHub credentials will be automatically selected in the Git Credentials dropdown if you added them earlier.
-
-
Select the Owner/Organization where the new GitHub repository will be created
-
Enter a Repository Name.
-
Choose the Repository Visibility setting (Public or Private).
-
Click Create.
Once the project is created, Domino will have created a repository in GitHub that is now linked to the project. This confirms that your credentials and token are working correctly.
If the PAT is configured properly, Domino will:
-
Create a new Domino project.
-
Create a new GitHub repository.
-
Link the two together.
Sometimes the setup doesn’t go smoothly. If you run into issues, here are a few common things to check:
-
Invalid or expired token
-
Make sure you copied the entire PAT when you generated it.
-
If the token has expired, generate a new one and update your Domino Git Credentials.
-
-
Missing scopes
-
If repository creation fails, verify that your PAT includes at least the repo and workflow scopes.
-
For evaluation setups, selecting all scopes avoids scope-related errors.
-
-
Incorrect credentials in Domino
-
Open Account Settings > Git Credentials.
-
Confirm that the saved username matches your GitHub account and the token is correct.
-
-
Network or access restrictions
-
Verify that your Domino environment can reach github.com.
-
If using an enterprise firewall or VPN, confirm that GitHub is not being blocked.
-
You’ve now linked your GitHub account to Domino and verified the connection by creating a test project and repository. With this setup, Domino can automatically create and manage GitHub repositories for your projects, keeping your code versioned and accessible.
-
Use Git-based projects or import Git repositories to use in your Workspace.
