Domino Datasets provides high-performance, versioned, and structured filesystem storage in Domino. You can use Datasets to build multiple curated collections of data in one Project and share them with your collaborators to use in their Projects. Likewise, you can mount Datasets from other Projects in your own Project if they are shared with you. You can modify the contents of a Dataset through the Domino application or through workload executions.
A Dataset always reflects the most recent version of the data. For reproducibility, you can create read-only snapshots of your Dataset at any moment in time. Snapshots are associated with the Dataset they version.
You can have five Datasets in a Project, by default. Your administrator configures this using the read-write Datasets Central Configuration settings.
If the Dataset you need is not yet in Domino, you can create it in your Project:
-
In the navigation pane, click Data, then click Create New Dataset.
-
Enter a Name and Description, then click Create Dataset.
Create a new Dataset from a snapshot
You can create as many snapshots as you need, but you cannot modify existing snapshots. Instead, you can create a Dataset from an existing snapshot, modify the new Dataset, and then create a new snapshot:
-
Go to the existing snapshot.
-
Click Copy to New Dataset.
-
Complete the fields as needed.
-
Click Upload files to add files to the Dataset.
-
Click Take Snapshot > Include all files.
Upload files to a Dataset
Use the Domino UI to upload up to 50GB or 50,000 individual files. For larger uploads, use the Domino CLI for your upload.
-
In your Project, go to Data > Domino Datasets.
-
Open the Dataset to which you want to add files, then click Upload files:
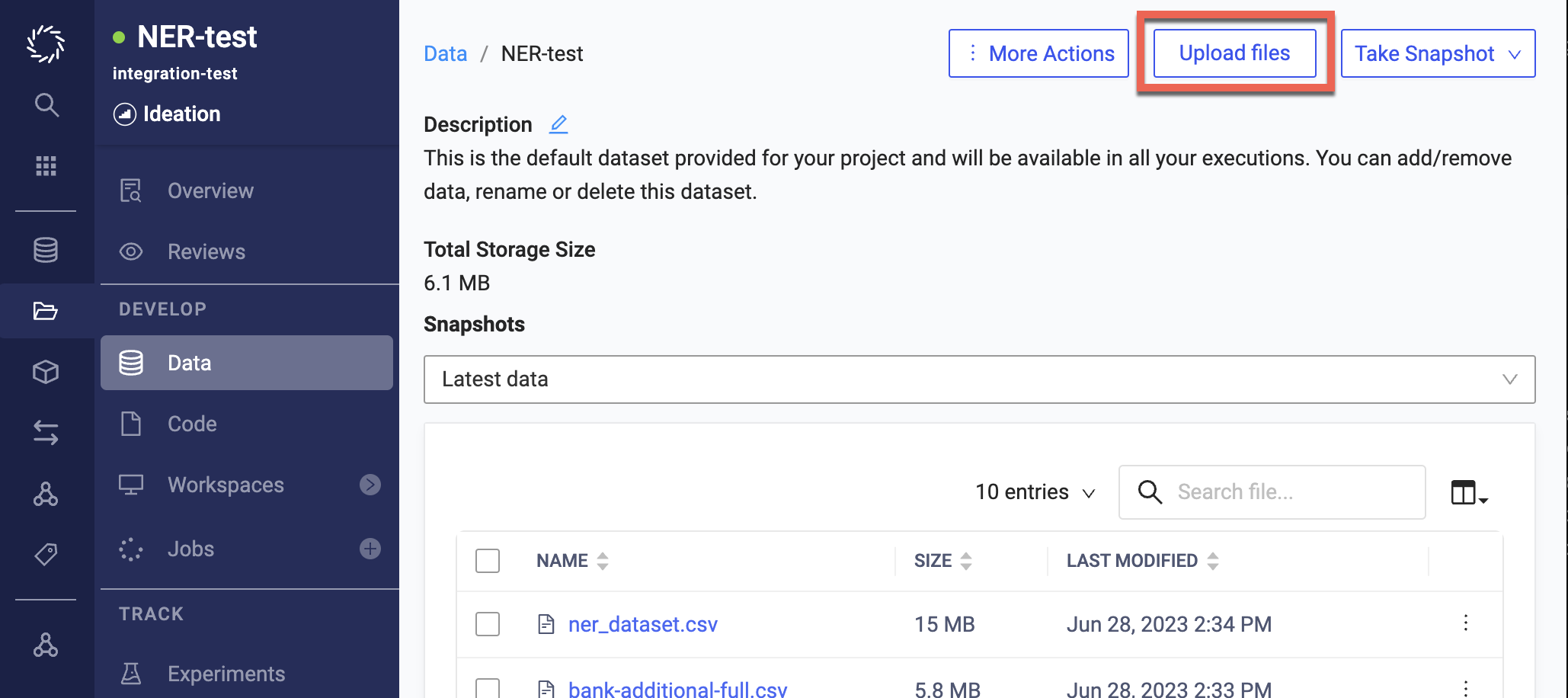
You can browse your local filesystem or drag and drop files to upload.
TipTo preserve the filesystem structure of your uploads, use the drag-and-drop option. You can pause and resume the upload as needed.
Download files from Datasets
Use the Domino CLI to download files and folders from your Projects.
download will download the latest copy of your files from the cloud into your current project folder.
If you have made changes that conflict with changes in the cloud, you will see both versions of the conflicting file side-by-side.
There are two reasons files in the cloud might change: first, your collaborators on a Project might make changes; second, you might have executed a run that produced new output files.
domino downloadTo download the output files of the given run, please see the Download files with the CLI page.
If you don’t have the CLI installed, see Install the Domino Command Line (CLI) for instructions.
You can always modify the contents of a Dataset or rename the Dataset.
|
Tip
| Always create a snapshot before modifying the contents of a Dataset so that you can always return to the previous version of the data. |
Delete a Dataset
If you no longer need the entire Dataset, you can mark it for deletion. When you mark a Dataset for deletion, it removes the Dataset and its associated snapshots from the originating Project and from all projects that it was shared with. Domino executions will not be able to use the Dataset. A Domino administrator must perform the final deletion.
-
In the navigation pane, click Data, then click the name of the Dataset to delete.
-
Click Delete Dataset.
-
Click Delete Dataset to confirm that you want to mark the Dataset for deletion. Your administrator will permanently delete the Dataset.
Add or remove files
You can add or delete files in a Dataset using the Domino UI. With the CLI, you can add all the files in a folder to a Dataset.
In the navigation pane, click Data, then click the name of the Dataset to change.
-
To add files, click Upload files.
-
To delete files, select the files to delete, then click Delete Selected Items.
-
To rename the Dataset, click Rename Dataset, enter the new name, then click Rename.
Before deleting a file with a special character like a backslash (\) in its name, you need to rename it first. You can use a tilde (~) or colon (:) anywhere in a filename, except at the beginning. If the file that you want to delete has a tilde or colon at the beginning of its name, rename it.
Rename files and folders
You can change the name of the latest version of a file or folder in a Dataset. Domino also does not rename files or folders in snapshots.
|
Warning
| You must update references to the original file or folder. If you don’t, your Project might not work. For example, you might see inconsistencies in text files and documentation. |
-
Go to a Project that uses a Dataset.
-
In the navigation pane, click Data.
-
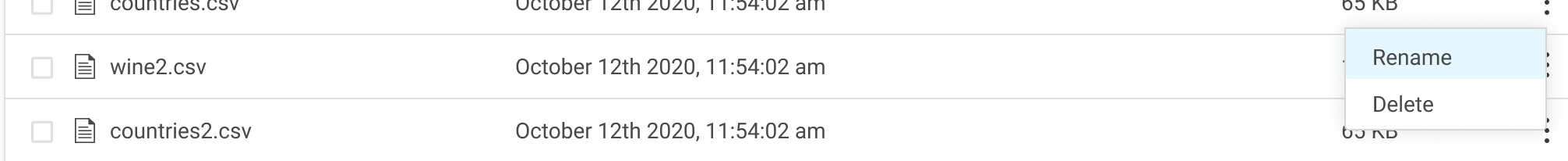
To rename the file or folder, go to the end of the row and click the three vertical dots.
-
Click Rename.
-
In the Rename window, enter the New Name and click Rename.
If you have data in an external source from which you want to periodically fetch and load into Domino, you can set up scheduled jobs to write to Datasets.
Suppose you have data stored in an external Data Source that is periodically updated. If you wanted to fetch the latest state of that file once a week and load it into a Domino Dataset, you could set up a scheduled Run:
-
Create a Dataset to store the data from the external source.
-
Write a script that fetches the data and writes it to the Dataset.
-
Create a scheduled Job to run your script with the new Dataset configuration.
The following is a detailed example showing how to fetch a large, dynamic data file from a private S3 bucket with a scheduled Run once a week.
-
Create a Dataset to hold the file. This example shows the Dataset named
fetched-from-s3.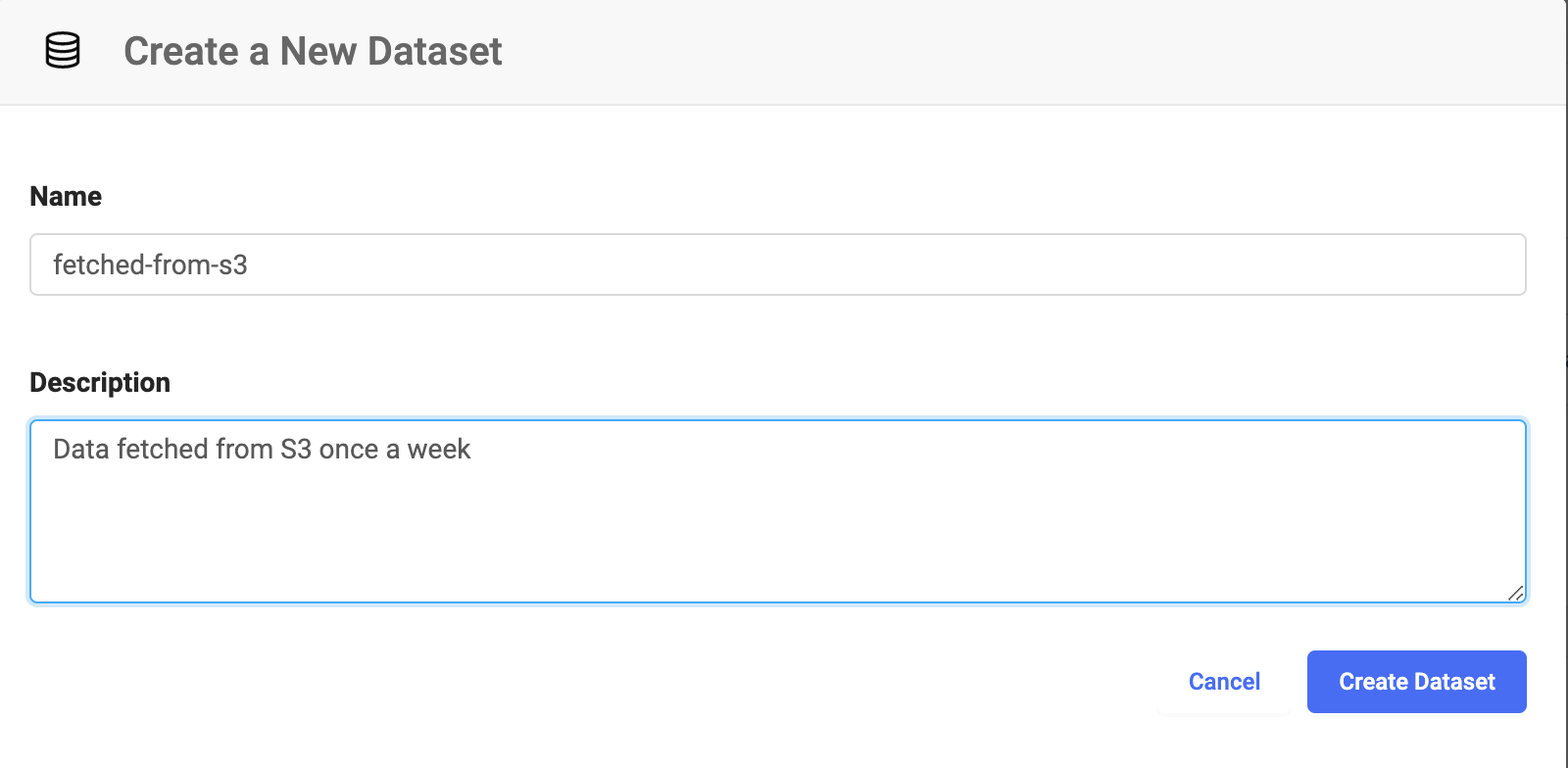
For this example, assume the S3 bucket is named
my_bucketand the file you want is namedsome_data.csv. You can set up your script like this:fetch-data.pyimport boto3 import io # Create new S3 client client = boto3.client('s3') # Download some_data.csv from my_bucket and write to latest-S3 output mount file = client.download_file('my_bucket', 'some_data.csv', '/domino/datasets/fetched-from-s3/some_data.csv') -
Set up a scheduled Job that executes this script once a week with the correct Dataset configuration.