Make sure you have a good understanding of the key concepts before you get started with Domino Flows.
This section demonstrates a basic example that:
-
Takes two integers as an input to a flow.
-
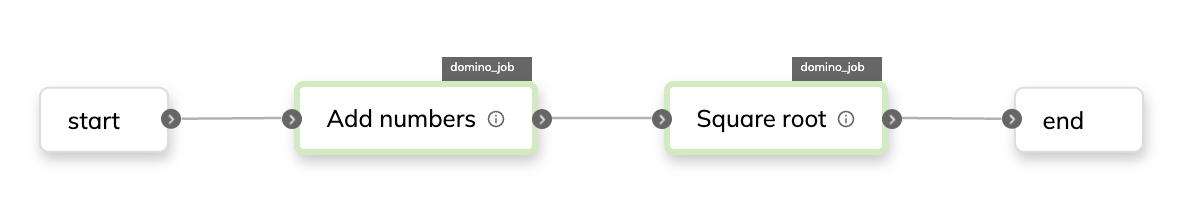
The first task adds the integers together and passes the result as an input to the second task.
-
The second task takes the square root of the input and returns the result as the final output of the flow.
This example flow can be visualized as follows:
To create a Domino Flow:
-
Create a workspace using the Domino Standard Environment (DSE), or a custom environment that is built on top of the DSE.
-
Create a file named
add.pyin the root directory. Add the following code to the file to add two integer inputs together:from pathlib import Path # Read inputs a = Path("/workflow/inputs/first_value").read_text() b = Path("/workflow/inputs/second_value").read_text() # Calculate sum sum = int(a) + int(b) print(f"The sum of {a} + {b} is {sum}") # Write output Path("/workflow/outputs/sum").write_text(str(sum)) -
Create a file named
sqrt.pyin the root directory. Add the following code to the file to calculate the square root of the input:from pathlib import Path # Read input value = Path("/workflow/inputs/value").read_text() # Calculate square root sqrt = int(value) ** 0.5 print(f"The square root of {value} is {sqrt}") # Write output Path("/workflow/outputs/sqrt").write_text(str(sqrt)) -
Create a file named
workflow.pyin the root directory. Add the following code to the file to define the flow:from flytekit import workflow from flytekitplugins.domino.task import DominoJobConfig, DominoJobTask @workflow def simple_math_workflow(a: int, b: int) -> float: # Create first task add_task = DominoJobTask( name='Add numbers', domino_job_config=DominoJobConfig(Command="python add.py"), inputs={'first_value': int, 'second_value': int}, outputs={'sum': int}, use_latest=True ) sum = add_task(first_value=a, second_value=b) # Create second task sqrt_task = DominoJobTask( name='Square root', domino_job_config=DominoJobConfig(Command="python sqrt.py"), inputs={'value': int}, outputs={'sqrt': float}, use_latest=True ) sqrt = sqrt_task(value=sum) return sqrt -
Commit the code and run the following command in the Workspace terminal to register and run the flow:
pyflyte run --remote workflow.py simple_math_workflow --a 10 --b 6 -
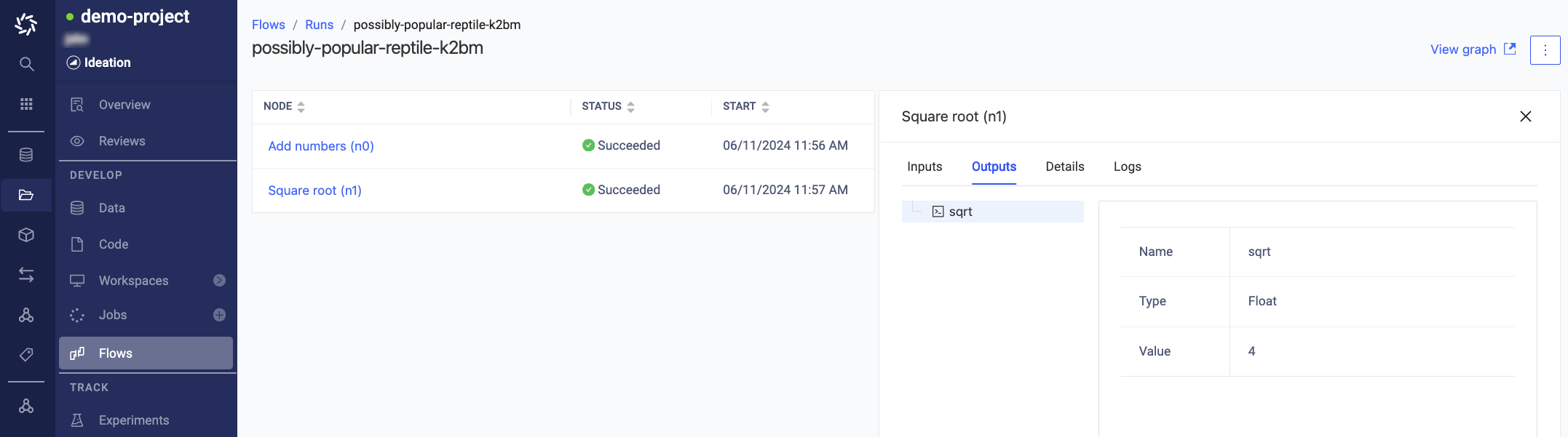
Once you run the command above, navigate to Flows > Runs > Run Name in the Domino UI to monitor the results and view the outputs that were produced by the execution.
-
To visualize the full execution flow, click the View graph button to navigate to the Flyte UI.
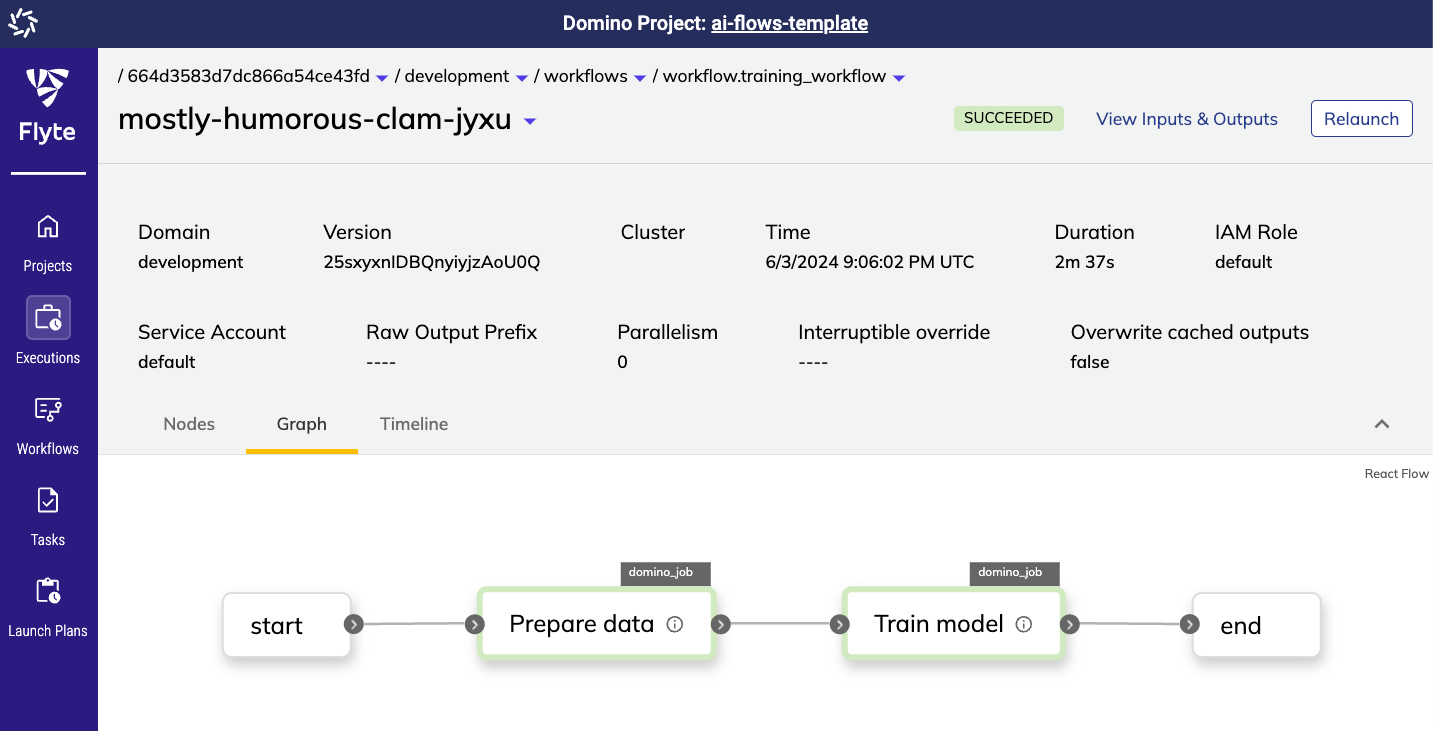
Rather than beginning from scratch, you can start from a pre-built template in the AI project hub. This section uses a template that demonstrates a basic training flow example:
-
It takes the path to a dataset as an input to a flow.
-
The first task does some basic data processing and returns a CSV file that gets passed as input to the next task.
-
The second task takes the CSV file and uses it to train a model that is returned as the output to the flow.
The training flow can be visualized as follows:
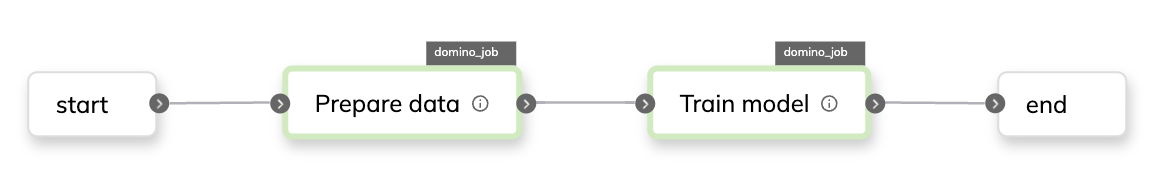
To create a training flow:
-
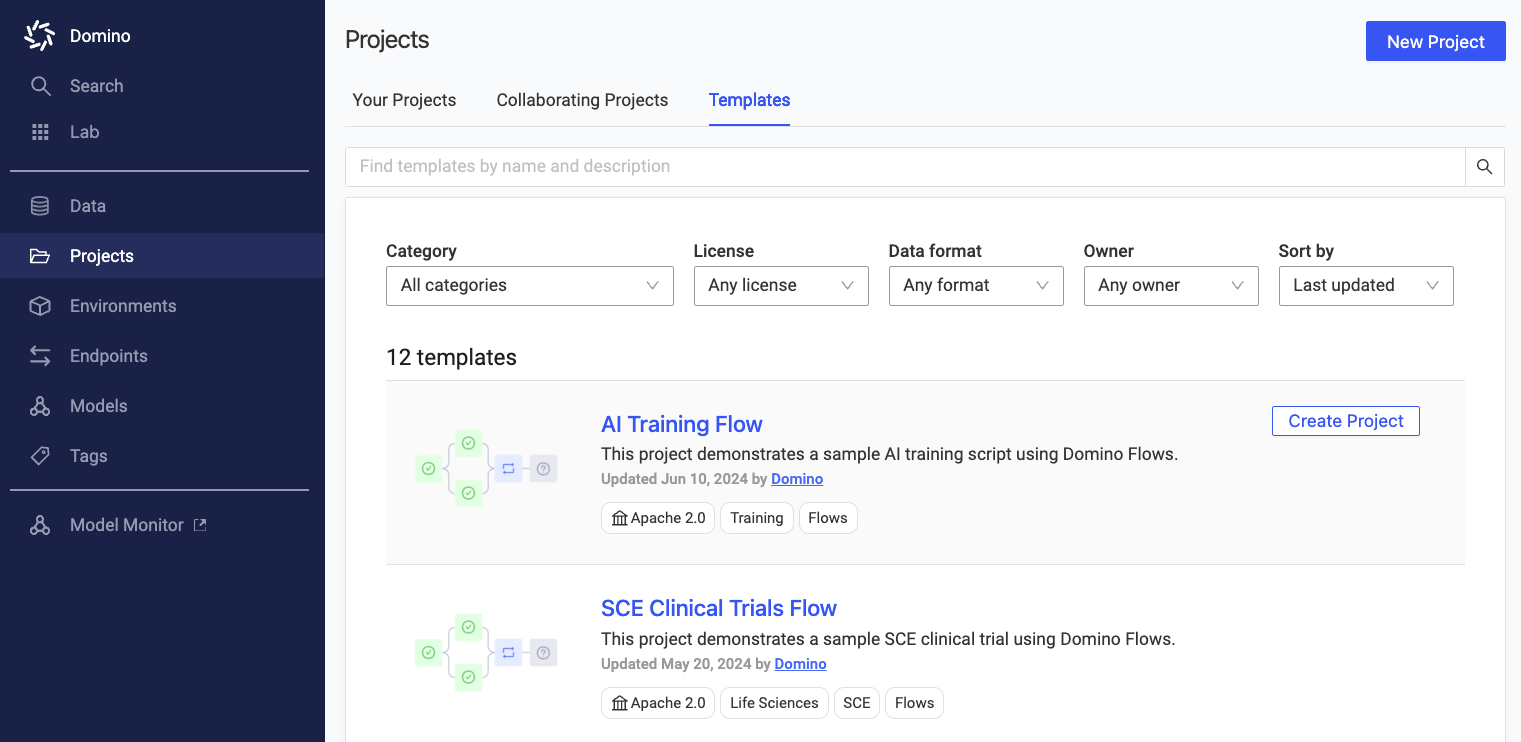
Go to AI Hub and select the AI Training Flow template. Create a Project from this template.
-
Create a Workspace using the Domino Standard Environment (DSE), or a custom environment that is built on top of the DSE.
-
Inspect the
workflow.pyfile for the definition of the flow. Note how a helper method calledrun_domino_job_taskis used here instead of theDominoJobConfigandDominoJobTaskin the basic example above.data_prep_results = run_domino_job_task( flyte_task_name="Prepare data", command="python /mnt/code/scripts/prep-data.py", environment_name="Domino Standard Environment Py3.11 R4.4", hardware_tier_name="Small", inputs=[ Input(name="data_path", type=str, value=data_path) ], output_specs=[ Output(name="processed_data", type=FlyteFile[TypeVar("csv")]) ], use_project_defaults_for_omitted=True ) training_results = run_domino_job_task( flyte_task_name="Train model", command="python /mnt/code/scripts/train-model.py", environment_name="Domino Standard Environment Py3.11 R4.4", hardware_tier_name="Small", inputs=[ Input(name="processed_data", type=FlyteFile[TypeVar("csv")], value=data_prep_results['processed_data']), Input(name="epochs", type=int, value=10), Input(name="batch_size", type=int, value=32) ], output_specs=[ Output(name="model", type=FlyteFile) ], use_project_defaults_for_omitted=True ) -
Run the following command in the Workspace terminal to register and run the flow:
pyflyte run --remote workflow.py training_workflow --data_path /mnt/code/data/data.csv -
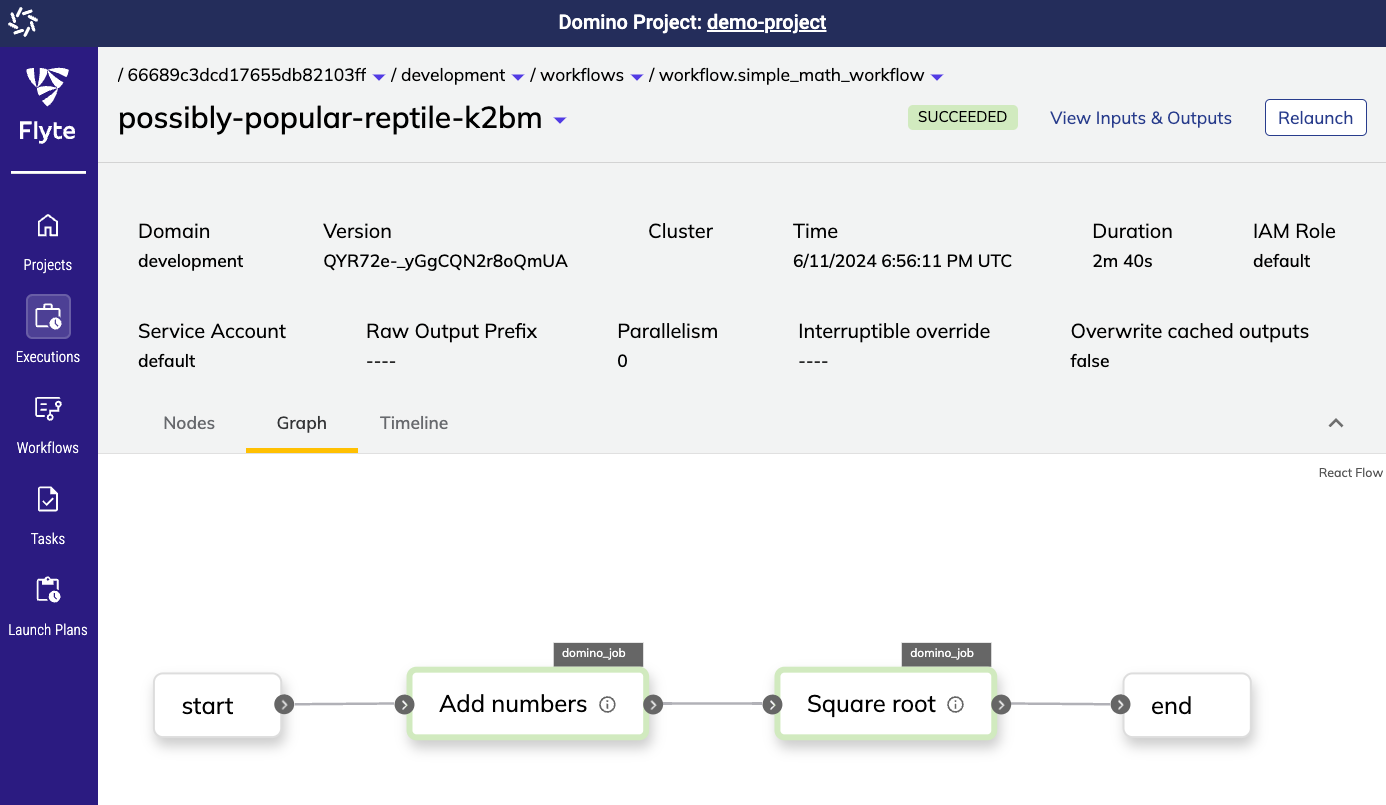
Navigate to Flows > Runs > Run name to monitor the results and view the outputs that were produced by the execution.
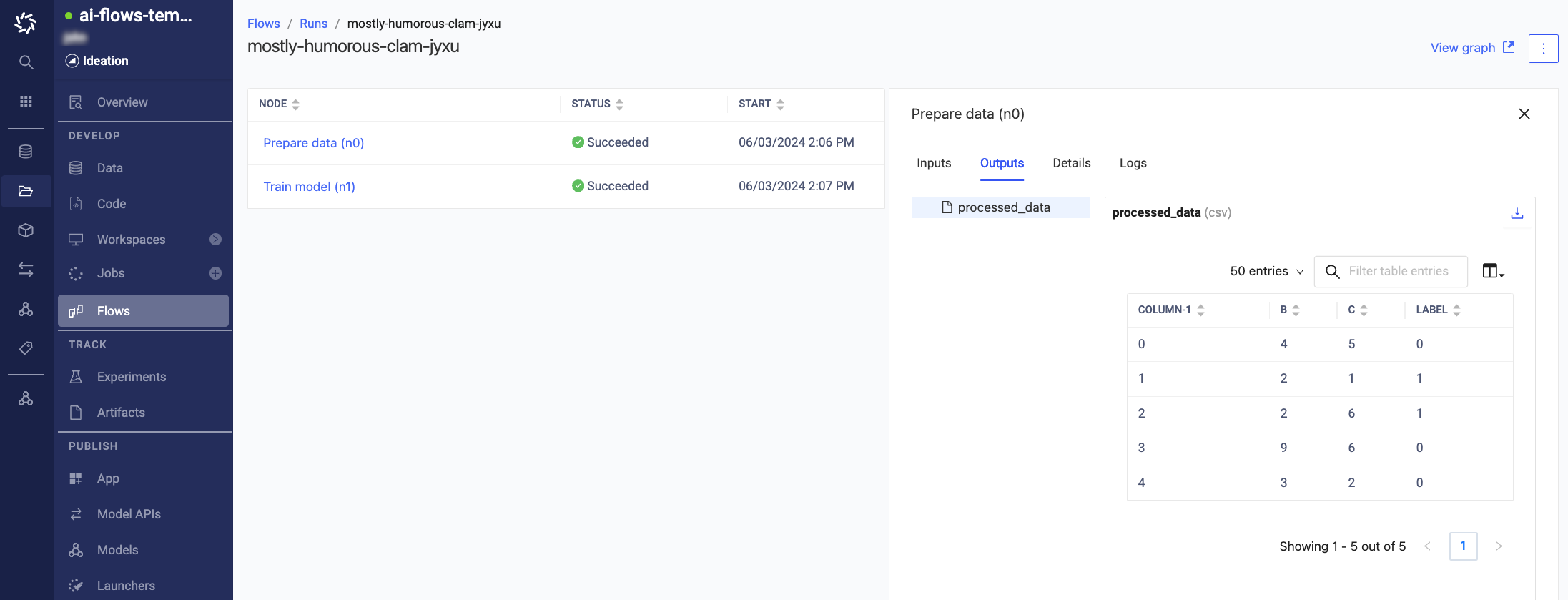
-
To visualize the full execution flow, click the View graph button to navigate to the Flyte UI.