This topic describes how to connect to MySQL from Domino. You must have network connectivity between MySQL and your Domino deployment.
The easiest way to connect to MySQL from Domino is to create a Domino Data Source as described below.
-
From the navigation pane, click Data.
-
Click Create a Data Source.
-
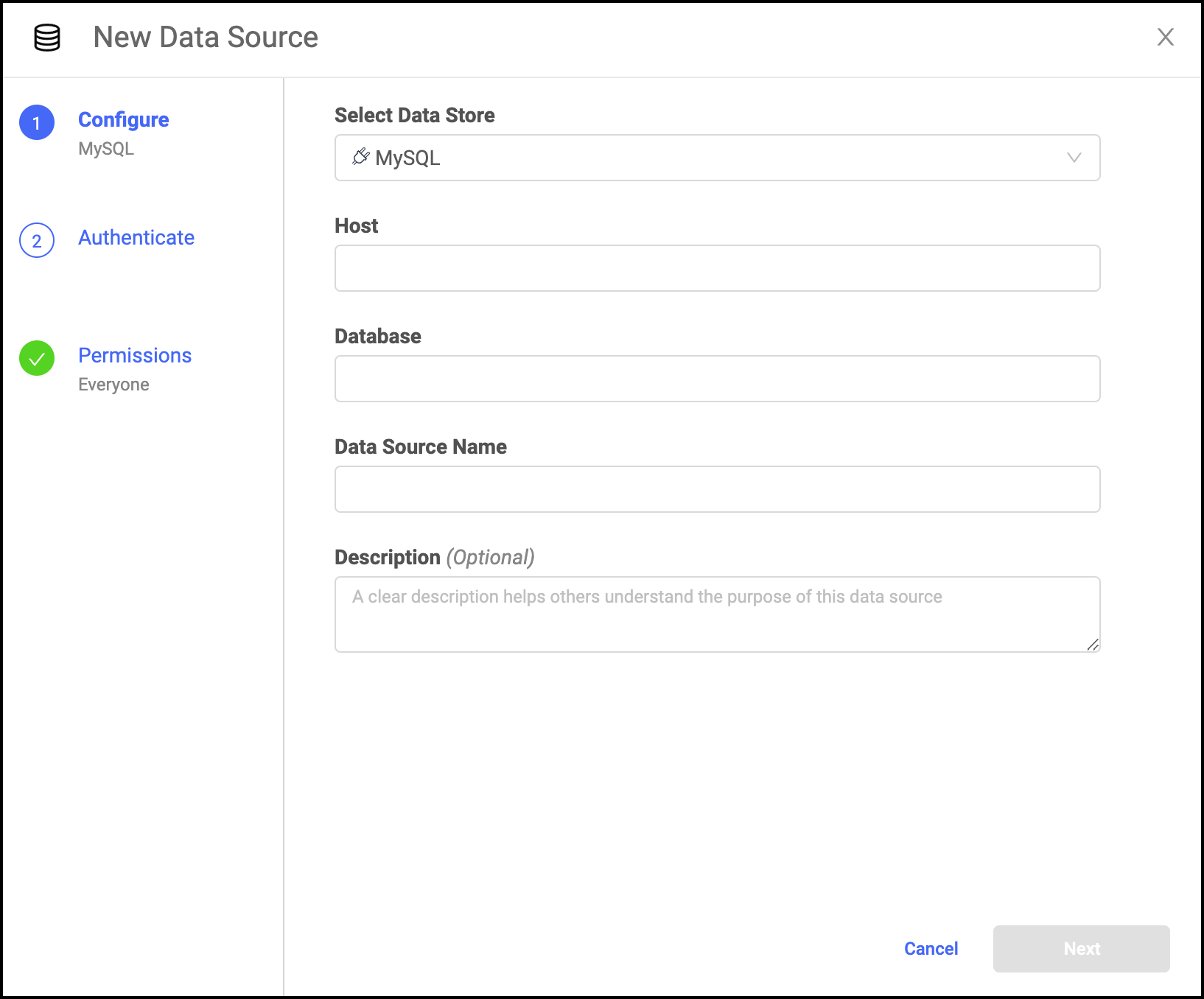
In the New Data Source window, from Select Data Store, select MySQL.
-
Enter the Host. Valid values are
<host string>:<port>or<host string>.If no port is specified, the default is 3306.
-
Enter the name of the Database.
-
Enter the Data Source Name.
-
Optional: Enter a Description to explain the purpose of the Data Source to others.
-
Click Next.
-
Specify the credentials for authenticating to MySQL.
Basic authentication is supported by default. IAM credential propagation might also be available if your administrator has enabled it.
NoteIAM-authenticated connections can be used only for executing jobs and workspaces. Other execution types, such as scheduled jobs and Model APIs, require basic authentication. -
Click Next (or Skip for Now to configure authentication later).
-
Select whether Everyone can access this Data Source or just Specific users or organizations.
-
Select who can view and use the Data Source in projects.
-
Click Finish Setup.
|
Warning
| This section describes an alternate method to connect to the MySQL Data Source. Domino does not officially support this method. |
-
Domino recommends the mysql-connector-python library to interact with MySQL databases from Python.
-
Use the following Dockerfile instruction to install psycopg2 in your environment. You must have pip installed.
USER root RUN pip install mysql-connector-python USER ubuntu -
You must set up the Domino environment variables to store secure information about your MySQL connection.
-
MYSQL_HOSTHostname where your MySQL service is running. Make sure your MySQL service and network firewall are configured to accept connections from Domino.
-
MYSQL_USERThe MySQL user you want to authenticate as.
-
MYSQL_PASSWORDThe password for the user chosen previously.
See Secure Credential Storage to learn more about Domino environment variables.
-
-
See the mysql-connector-python documentation for information about how to use the package. The following is an example to connect to MySQL with
mysql-connector-pythonwhere:-
You have set up environment variables with the host, user, and password.
-
Your user has access to a database named
db1in the target MySQL instance. -
The
db1database contains a table calledemployees.from mysql.connector import (connection) import os # fetch values from environment variables and set the target database hostname = os.environ['MYSQL_HOST'] username = os.environ['MYSQL_USER'] password = os.environ['MYSQL_PASSWORD'] dbname = 'db1' # establish connection to db1 database in your mysql service cnx = connection.MySQLConnection(user=username, password=password, host=hostname, database=dbname) # create cursor for passing queries to database cursor = cnx.cursor() # define query query = ("SELECT * FROM employees") # execute query cursor.execute(query) # print results for row in cursor: print(row) # close connection cnx.close()
-
R and RMySQL
-
To interact with MySQL services from R, Domino recommends the RMySQL library.
-
Use the following Dockerfile instructions to add RMySQL to your environment.
RUN sudo apt-get install -y libmariadb-client-lgpl-dev RUN R -e 'install.packages("RMySQL")' -
Set the following Domino environment variables to store secure information about your MySQL connection.
-
MYSQL_HOSTHostname where your MySQL service is running. Make sure your MySQL service and network firewall are configured to accept connections from Domino.
-
MYSQL_USERThe MySQL user you want to authenticate as.
-
MYSQL_PASSWORDThe password for the user chosen previously.
See Secure Credential Storage to learn more about Domino environment variables.
-
-
See the RMySQL documentation for information about how to use the package. The following is an example for connecting to MySQL with RMySQL where:
-
You have set up environment variables with the host, user, and password.
-
Your user has access to a database named
db1in the target MySQL instance. -
The database contains a table named
employees.# load the library library(RMySQL) # fetch values from environment variables and set the target database hostname <- Sys.getenv['MYSQL_HOST'] username <- Sys.getenv['MYSQL_USER'] password <- Sys.getenv['MYSQL_PASSWORD'] database <- 'db1' # set up a driver and use it to create a connection to your database con <- dbConnect(RMySQL::MySQL(), host = hostname, user = username, password = password, dbname = database) # run a query and load the response into a dataframe df_mysql <- dbGetQuery(con, "SELECT * FROM employees") # close your connection when finished dbDisconnect(con)
-
-
After connecting to your Data Source, learn how to Use Data Sources.
-
Share this Data Source with your collaborators.
