This is a simple example on how to host a HTML page on Domino. There are a number of ways to host web applications of course but this example shows how you can integrate a simple HTTP server using python with Domino. You could also add javascript and other pages to your project. The example in this note just shows how you would start the server to support your pages.
You’ll need to create two files in your project (in addition to your files required for your page such as index.html).
app.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
python ./app.pyapp.py
import http.server
import socketserver
PORT = 8888
Handler = http.server.SimpleHTTPRequestHandler
httpd = socketserver.TCPServer(("", PORT), Handler)
print ("serving at port", PORT)
httpd.serve_forever()The app.sh file
When you publish an app, Domino looks for an app.sh file in your project to find the launch instructions. Aside from the app.sh file, Domino’s app development process mirrors standard development so your apps are portable and can be deployed elsewhere. Just include your app’s files in your Domino project.
When Domino launches your app, it runs the app.sh file within the container that contains your project files. The app.sh file must contain the commands to start the web hosting process.
|
Note
|
Domino requires this configuration for app service: 0.0.0.0 on port 8888.
If your hosting network uses a different default, specify that default in your app.sh file or some alternate configuration.
|
-
Click Publish from the project sidebar.
-
Give your app an informative title and description, and set permissions to Anyone can access. This allows anyone with a network connection to your Domino deployment to access the app if they have the URL.
TipLeave Show in Launchpad selected to make your app easily discoverable. You can always change this later. 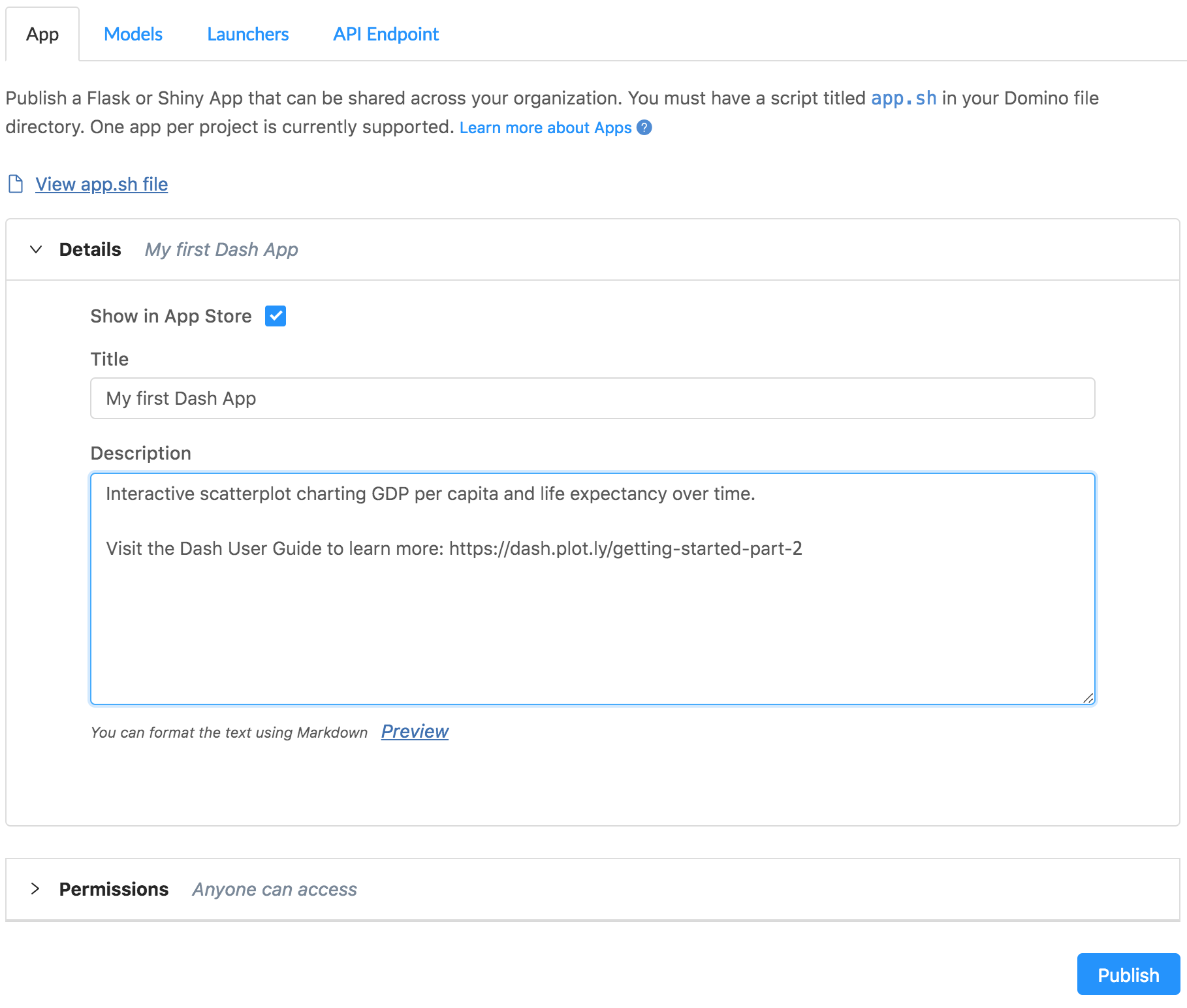
-
Click Publish.
-
After the app status says "Running", click View App to load your App.
