A complex flow may execute many steps, producing hundreds of outputs, the majority of which are typically intermediate computations and not final results. It therefore becomes useful to elevate outputs of flow executions to easily discover, reuse, and inspect them, including the lineage of how they were produced. These task or workflow outputs are called Flow Artifacts.
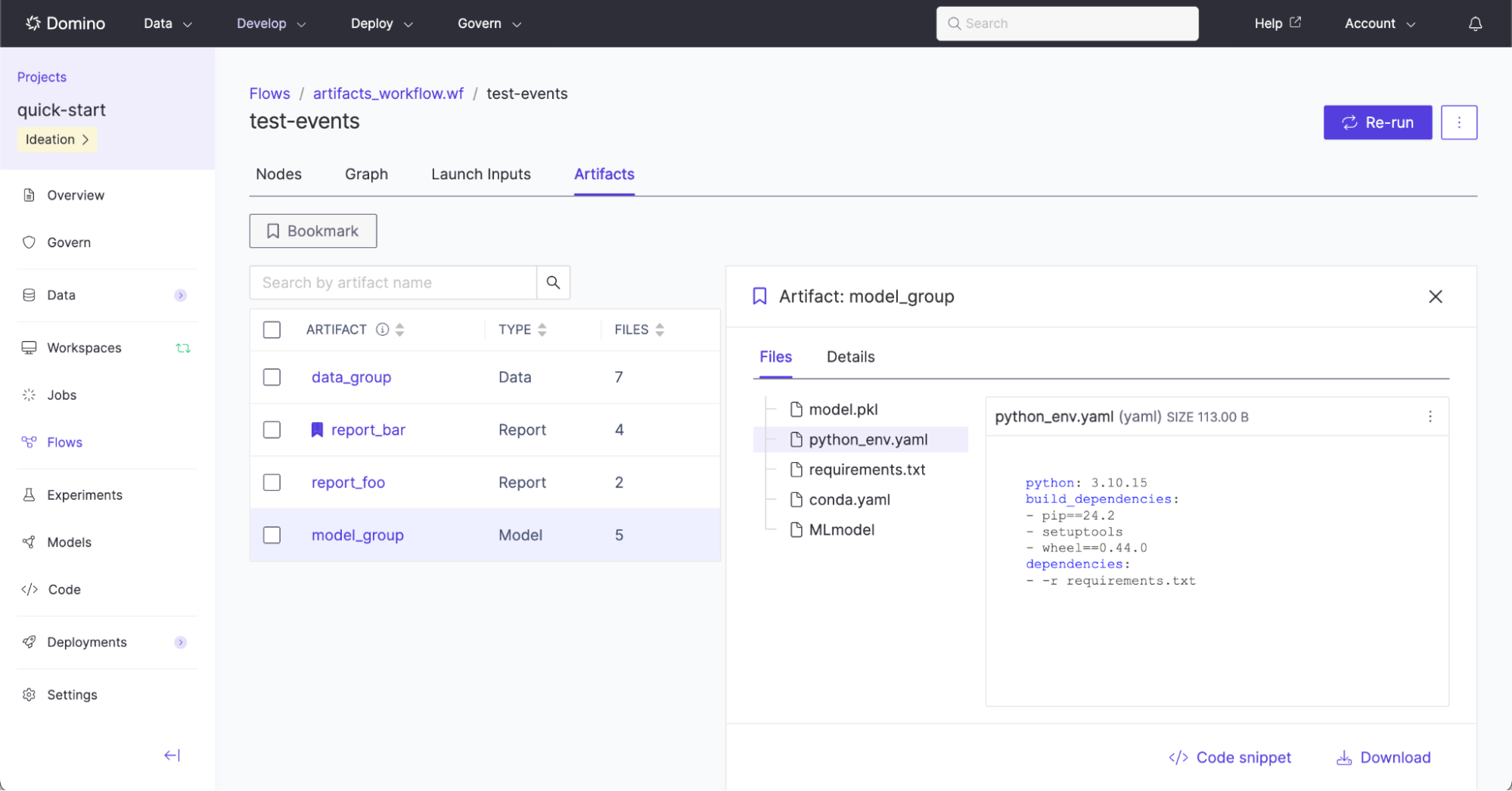
Flow Artifacts are explicitly defined in code by flow definition authors.
The Artifact method is used to generate a named artifact. The named artifact can have individual files added to it anywhere in the workflow definition. Typically an Artifact is declared at the beginning of a workflow like this:
PickleArtifact = Artifact(name="Pytorch Model", type=MODEL)In any part of a workflow where an output might be used, the .File(name="file.ext") method can be called to declare that the output is an Artifact. For example:
@workflow
def single_model() -> PickleArtifact.File(name="model.pkl"):There are 3 types of Flow Artifacts:
-
DATAartifact: Files that may be added later as a new dataset snapshot. -
MODELartifact: Files that may later be registered as a model. -
REPORTartifact: Files that may be part of a collection that make up a report.
In the following example, DataArtifact.File(name="data.csv") adds a FlyteFile output from the data_prep_job to the Flow Artifact declared as Artifact(name="My Data", type=DATA). Unlike the use of FlyteFile[TypeVar("csv")] from previous examples, Flow Artifact files automatically infer their type from the given file extension.
from flytekit import workflow
from flytekit.types.file import FlyteFile
from flytekitplugins.domino.task import DominoJobConfig, DominoJobTask
from flytekitplugins.domino.artifact import Artifact, DATA, MODEL, REPORT
# define the artifact name and type which may be REPORT, DATA or MODEL
DataArtifact = Artifact(name="My Data", type=DATA)
ModelArtifact = Artifact(name="My Model", type=MODEL)
@workflow
def training_workflow(data_path: str) -> ModelArtifact.File(name="model.pt"):
data_prep_job_config = DominoJobConfig(Command="python prep-data.py")
data_prep_job = DominoJobTask(
name='Prep data',
domino_job_config=data_prep_job_config,
inputs={'data_path': str},
outputs={'processed_data': DataArtifact.File(name="data.csv")},
use_latest=True
)
data_prep_results = data_prep_job(data_path=data_path)
training_job_config = DominoJobConfig(Command="python train-model.py")
training_job = DominoJobTask(
name='Train model',
domino_job_config=training_job_config,
inputs={'processed_data': FlyteFile[TypeVar("csv")]},
outputs={'model': FlyteFile[TypeVar("pt")]},
use_latest=True
)
training_results = training_job(processed_data=data_prep_results["processed_data"])
return training_results["model"] # Final output is returned hereThere are no limits to the number of Flow Artifacts that can be defined, the number of files that can be added to each Flow Artifact, or where the Flow Artifact files are created. However, an individual Flow Artifact cannot include the same filename more than once. The following is not permitted because DataArtifact.File(name="data.csv") is used more than once:
DataArtifact = Artifact(name="My Data", type=DATA)
@workflow
def training_workflow(data_path: str) -> DataArtifact.File(name="data.csv"):
data_prep_job_config = DominoJobConfig(Command="python prep-data.py")
data_prep_job = DominoJobTask(
outputs={
# error - DataArtifact already has another data.csv
'raw_data': DataArtifact.File(name="data.csv"),
'processed_data': FlyteFile[TypeVar("csv")],
}
)
data_prep_results = data_prep_job(data_path=data_path)
return data_prep_results["processed_data"] # Final output is returned hereFlow Artifacts can be programmatically exported to Domino Datasets and NetApp Volumes. This is useful for enabling continuous, automated movement of new output data into Datasets and NetApp Volumes.
|
Note
|
When you include This design means that the visual placement of the launch node in the Graph view does not reflect the true ordering of when Flow Artifacts are exported. To verify export progress, open the separate export execution linked in the launch task’s logs. That execution contains detailed logs for each exported Flow Artifact. |
In the following example, DataArtifact.File(name="data.csv") is programmatically exported to the Domino Dataset with ID 681d3030ae3a706ef9c7f08b, and the NetApp Volume with ID 5d1204c2-24c8-47df-a47f-69185efa602b using the helper method run_launch_export_artifacts_task.
from flytekit import workflow
from flytekit.types.file import FlyteFile
from flytekitplugins.domino.task import DominoJobConfig, DominoJobTask
from flytekitplugins.domino.artifact import Artifact, DATA, ExportArtifactToDatasetsSpec, ExportArtifactToNetAppVolumesSpec, MODEL, REPORT, run_launch_export_artifacts_task
# define the artifact name and type which may be REPORT, DATA or MODEL
DataArtifact = Artifact(name="My Data", type=DATA)
ModelArtifact = Artifact(name="My Model", type=MODEL)
@workflow
def training_workflow(data_path: str) -> ModelArtifact.File(name="model.pt"):
data_prep_job_config = DominoJobConfig(Command="python prep-data.py")
data_prep_job = DominoJobTask(
name='Prep data',
domino_job_config=data_prep_job_config,
inputs={'data_path': str},
outputs={'processed_data': DataArtifact.File(name="data.csv")},
use_latest=True
)
data_prep_results = data_prep_job(data_path=data_path)
training_job_config = DominoJobConfig(Command="python train-model.py")
training_job = DominoJobTask(
name='Train model',
domino_job_config=training_job_config,
inputs={'processed_data': FlyteFile[TypeVar("csv")]},
outputs={'model': FlyteFile[TypeVar("pt")]},
use_latest=True
)
training_results = training_job(processed_data=data_prep_results["processed_data"])
# Programmatic export is enabled here
run_launch_export_artifacts_task(
spec_list=[
ExportArtifactToDatasetsSpec(
artifact=DataArtifact,
dataset_id="681d3030ae3a706ef9c7f08b",
),
ExportArtifactToNetAppVolumesSpec(
artifact=DataArtifact,
netapp_volume_id="5d1204c2-24c8-47df-a47f-69185efa602b",
target_relative_path="flows-data",
)
# ... More exports can be defined in this list, if needed.
],
environment_name="Domino Standard Environment",
hardware_tier_id="small-k8s",
use_project_defaults_for_omitted=True,
)
return training_results["model"] # Final output is returned hereThe helper method run_launch_export_artifacts_task performs the programmatic export.
It is required to specify this task to use the Domino Standard Environment (DSE) from 6.0 onwards, or a custom environment that is built on top of the DSE >= 6.0, as these contain the required Flyte Python and jq dependencies.
The full list of available parameters to the method run_launch_export_artifacts_task include:
| Parameter | Type | Description and Example |
|---|---|---|
spec_list | List[Union[ExportArtifactToDatasetsSpec, ExportArtifactToNetAppVolumesSpec]] | The list of specifications used to determine the Flows artifacts to be exported to the Domino Datasets and NetApp Volumes. |
use_project_defaults_for_omitted | bool | If set to |
environment_name | Optional[str] | Name of the Environment to use in the Domino Job. |
environment_id | Optional[str] | ID of the Environment to use in the Domino Job. This is recommended over using |
environment_revision_id | Optional[str] | A specific revisionId of the environment to use. |
hardware_tier_name | Optional[str] | Name of the hardware tier to use in the Domino Job. It is recommended to use a minimal-resource hardware tier. |
hardware_tier_id | Optional[str] | ID of the hardware tier to use in the Domino Job. This is recommended over using |
retries | int | Number of times to retry this task during a workflow execution. |
timeout | Union[timedelta, int] = timedelta(hours=3) | The maximum amount of time for which one execution of this task should be executed. The execution will be terminated if the runtime exceeds the given timeout. It is recommended to set this timeout duration to be greater than the workflow duration. |
-
Data artifact with a single file:
Example scenario: A flow produces a single ADaM dataset with the file name
adae.sas7bdatand the user wants to track the single file under its own data entity calledadae.Expand for example code.
from typing import TypeVar from flytekitplugins.domino.helpers import Output, run_domino_job_task from flytekitplugins.domino.artifact import Artifact, DATA from flytekit import workflow from flytekit.types.file import FlyteFile DataArtifact = Artifact("adae", DATA) @workflow def single_adam() -> DataArtifact.File(name="adae.sas7bdat"): return run_domino_job_task( flyte_task_name="Produce single ADaM Dataset", command="single_adam.py", output_specs=[ Output(name="adae", type=FlyteFile[TypeVar("sas7bdat")]), ], use_project_defaults_for_omitted=True, ) -
Data artifact with multiple files:
Example scenario: A flow produces multiple ADaM datasets (
adae.sas7bdat,advs.sas7bdat, andadsl.sas7bdat) and the user wants to track the collection of files under a single data entity calledadam.Expand for example code.
from typing import Tuple, TypeVar from flytekitplugins.domino.helpers import Output, run_domino_job_task from flytekitplugins.domino.artifact import Artifact, DATA from flytekit import workflow from flytekit.types.file import FlyteFile DataArtifact = Artifact("adam", DATA) @workflow def multiple_adam() -> Tuple[ DataArtifact.File(name="adae.sas7bdat"), DataArtifact.File(name="advs.sas7bdat"), # if name does not include the extension, then provide the type kwarg DataArtifact.File(name="adsl dataset", type="sas7bdat"), ]: # files in an Artifact can be produced by different Flows tasks # in this example, one task produces two of the files, and another task produces the third adae_dataset, advs_dataset = run_domino_job_task( flyte_task_name="Produce adae and advs Datasets", command="produce_adae_and_advs.py", output_specs=[ Output(name="adae", type=FlyteFile[TypeVar("sas7bdat")]), Output(name="advs", type=FlyteFile[TypeVar("sas7bdat")]), ], use_project_defaults_for_omitted=True, ) adsl_dataset = run_domino_job_task( flyte_task_name="Produce adsl Dataset", command="produce_adsl.py", output_specs=[ Output(name="adsl", type=FlyteFile[TypeVar("sas7bdat")]), ], use_project_defaults_for_omitted=True, ) return adae_dataset, advs_dataset, adsl_dataset -
Model artifact with a single file:
Example scenario: A flow produces a single model file with the name
model.pkland the user wants to track the single file as its own model entity.Expand for example code.
from typing import TypeVar from flytekitplugins.domino.helpers import Output, run_domino_job_task from flytekitplugins.domino.artifact import Artifact, MODEL from flytekit import workflow from flytekit.types.file import FlyteFile ModelArtifact = Artifact("My Model", MODEL) @workflow def single_model() -> ModelArtifact.File(name="model.pkl"): return run_domino_job_task( flyte_task_name="Produce model", command="produce_model.py", output_specs=[ # name of the Output can differ from the name of the ArtifactFile Output(name="my_model", type=FlyteFile[TypeVar("pkl")]), ], use_project_defaults_for_omitted=True, ) -
Model artifact with multiple files:
Example scenario: A flow produces multiple files relating to a model (
model.pkl,classes.txt) and the user wants to track the collection of files as a single model entity.Expand for example code.
from typing import Tuple, TypeVar from flytekitplugins.domino.helpers import Output, run_domino_job_task from flytekitplugins.domino.artifact import Artifact, MODEL from flytekit import workflow from flytekit.types.file import FlyteFile ModelArtifact = Artifact("My Model", MODEL) @workflow def multiple_model() -> Tuple[ ModelArtifact.File(name="model.pkl"), # if name does not include the extension, then provide the type kwarg ModelArtifact.File(name="classes", type="txt"), ]: return run_domino_job_task( flyte_task_name="Produce model with classes", command="produce_model_with_classes.py", output_specs=[ # name of the Output can differ from the name of the ArtifactFile Output(name="my_model", type=FlyteFile[TypeVar("pkl")]), Output(name="my_classes", type=FlyteFile[TypeVar("txt")]), ], use_project_defaults_for_omitted=True, ) -
Report artifact with a single file:
Example scenario: A flow produces a single TFL report with the file name
t_vscat.pdfand the user wants to track the single file as its own report entity.Expand for example code.
from typing import TypeVar from flytekitplugins.domino.helpers import Output, run_domino_job_task from flytekitplugins.domino.artifact import Artifact, REPORT from flytekit import workflow from flytekit.types.file import FlyteFile ReportArtifact = Artifact("TFL Report", REPORT) @workflow def single_report() -> ReportArtifact.File(name="t_vscat.pdf"): return run_domino_job_task( flyte_task_name="Produce PDF", command="produce_t_vscat.py", output_specs=[ Output(name="t_vscat", type=FlyteFile[TypeVar("pdf")]), ], use_project_defaults_for_omitted=True, ) -
Report artifact with multiple files:
Example scenario: A flow produces multiple TFL reports (
t_vscat.pdf,t_ae_rel.pdf) at different steps in the workflow and the user wants to track the collection of files as a single report entity.Expand for example code.
from typing import Tuple, TypeVar from flytekitplugins.domino.helpers import Output, run_domino_job_task from flytekitplugins.domino.artifact import Artifact, REPORT from flytekit import workflow from flytekit.types.file import FlyteFile ReportArtifact = Artifact("TFL Reports", REPORT) @workflow def multiple_report(): # files in an Artifact can be produced by different Flows tasks # in this example, one task produces one file, and another task produces the other vscat_pdf = run_domino_job_task( flyte_task_name="Produce vscat PDF", command="produce_t_vscat.py", output_specs=[ Output(name="t_vscat", type=ReportArtifact.File(name="t_vscat.pdf")), ], use_project_defaults_for_omitted=True, ) ae_rel_pdf = run_domino_job_task( flyte_task_name="Produce ae_rel PDF", command="produce_t_ae_rel.py", output_specs=[ # if name does not include the extension, then provide the type kwarg Output(name="t_ae_rel", type=ReportArtifact.File(name="t_ae_rel tfl report", type="pdf")), ], use_project_defaults_for_omitted=True, )
Find out more about how to inspect, bookmark, and declare Flow Artifacts in Examine Flow Artifacts.
Once you have properly defined the Flow and Flow Artifacts, learn how to:
