Train, evaluate, and deploy machine learning models through a unified no-code interface.
AutoML is a Domino extension that enables data scientists and domain experts to build, evaluate, and deploy machine learning models through a streamlined, no-code interface.
Powered by AutoGluon, AutoML automates the end-to-end model training pipeline - from data profiling and feature engineering through model selection, hyperparameter tuning, and ensembling - so you can go from raw data to a production-ready model in minutes.
AutoML provides two primary workflows:
-
Data Exploration: Upload a dataset, review column statistics and distributions, examine correlations, assess data quality, and apply transformations before training.
-
Model Training: Configure and run an AutoGluon training job that automatically trains multiple model types, ranks them on a leaderboard, and produces deployment-ready artifacts.
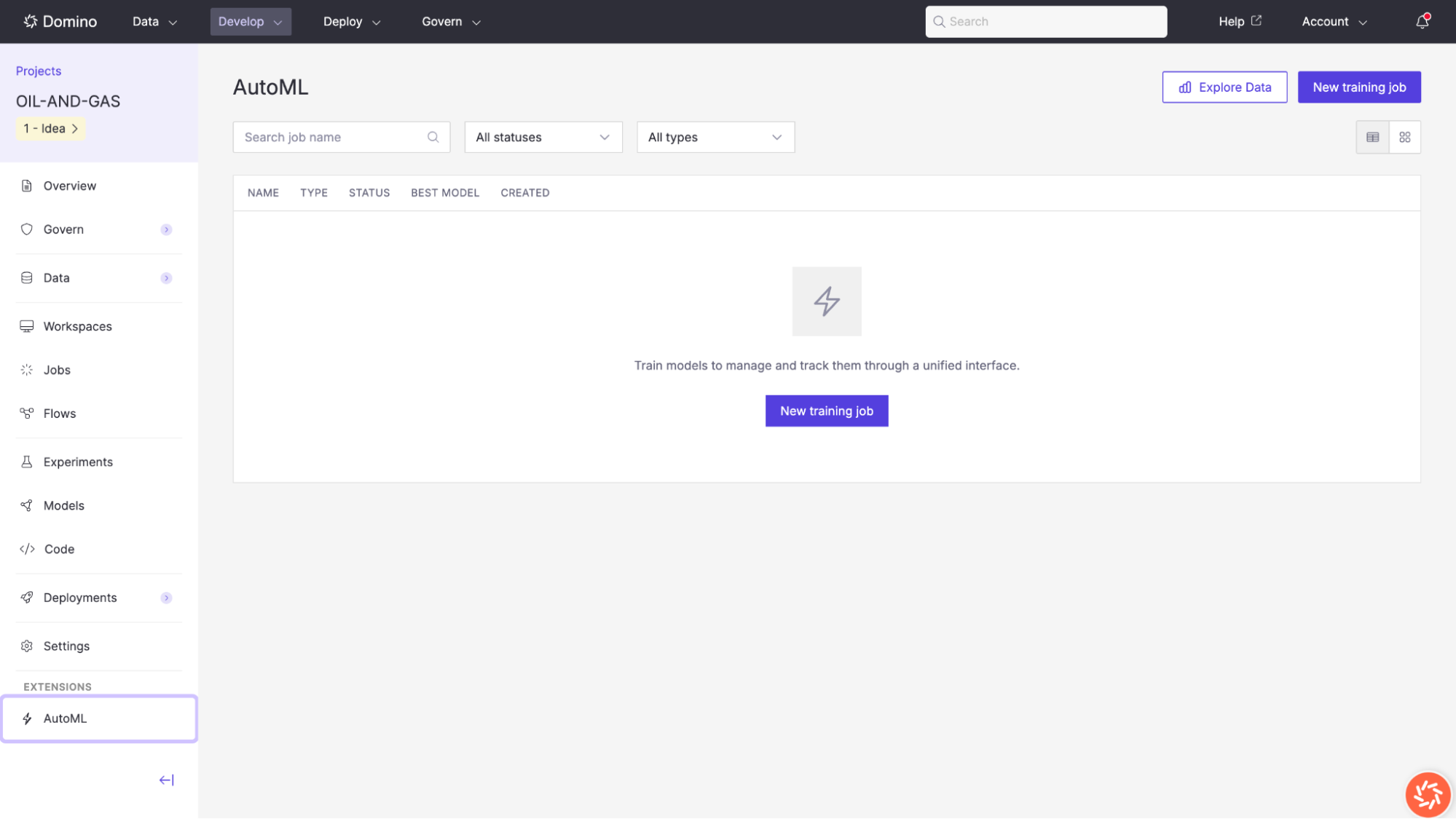
You can access AutoML from the left navigation sidebar of any Domino project under the Extensions section.
Access AutoML
-
Navigate to your Domino project.
-
In the left sidebar, scroll down to the Extensions section.
-
Click AutoML.
The AutoML landing page displays all existing training jobs with their name, type, status, best model, and creation date. From here you can start a new training job or explore your data.
|
Tip
| Use the Explore Data button in the top-right corner of the AutoML landing page to profile and transform your data before creating a training job. |
The Data Exploration tool lets you analyze data quality, distributions, and correlations, and prepare transformations before training a model.
To open it, click Explore Data from the AutoML landing page.
Upload data
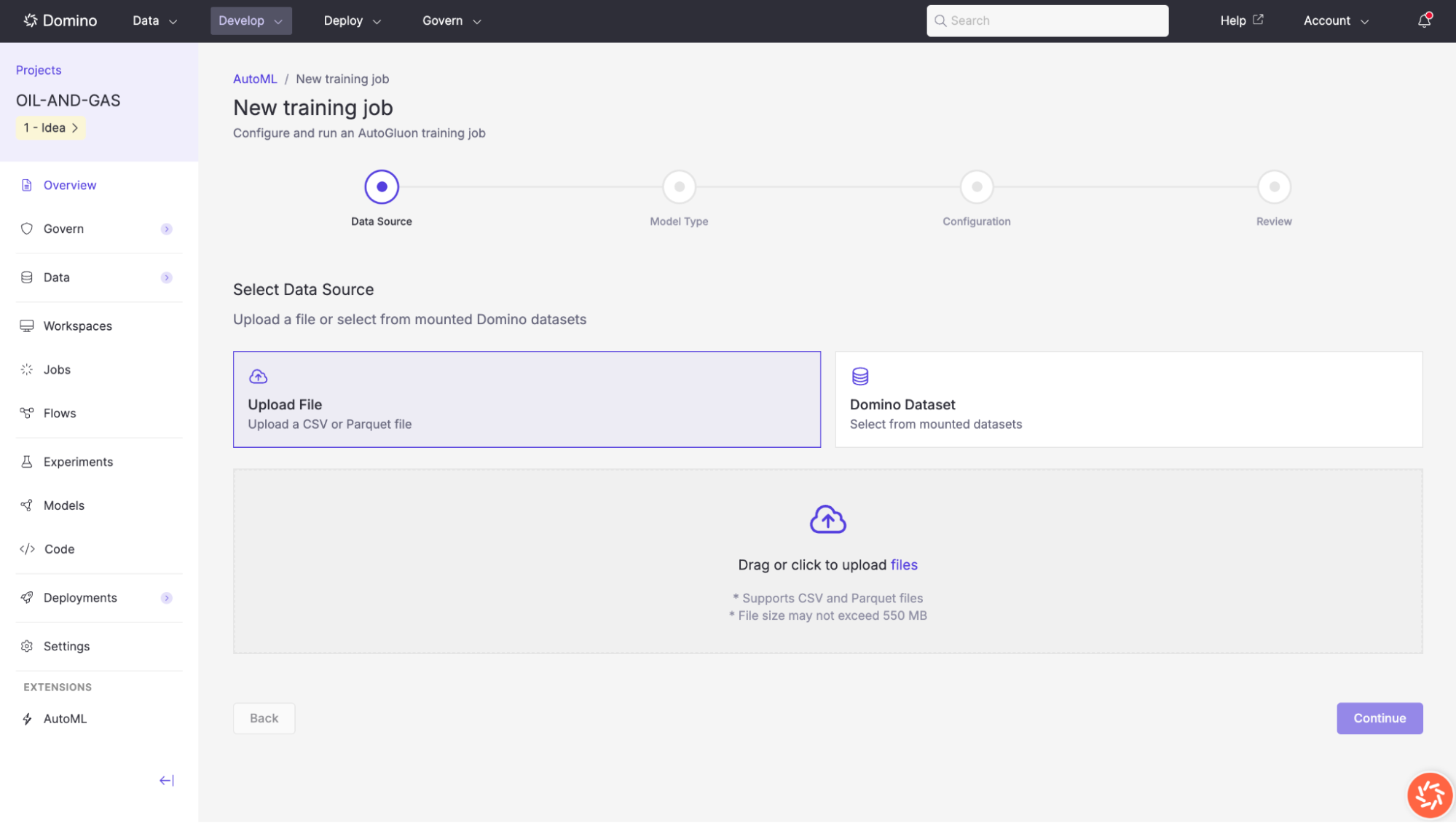
You can provide data in one of two ways:
-
Upload File: Drag and drop (or click to browse) a CSV or Parquet file. The maximum file size is 550 MB.
-
Domino Dataset: Select a file from a mounted Domino Dataset already connected to your project.
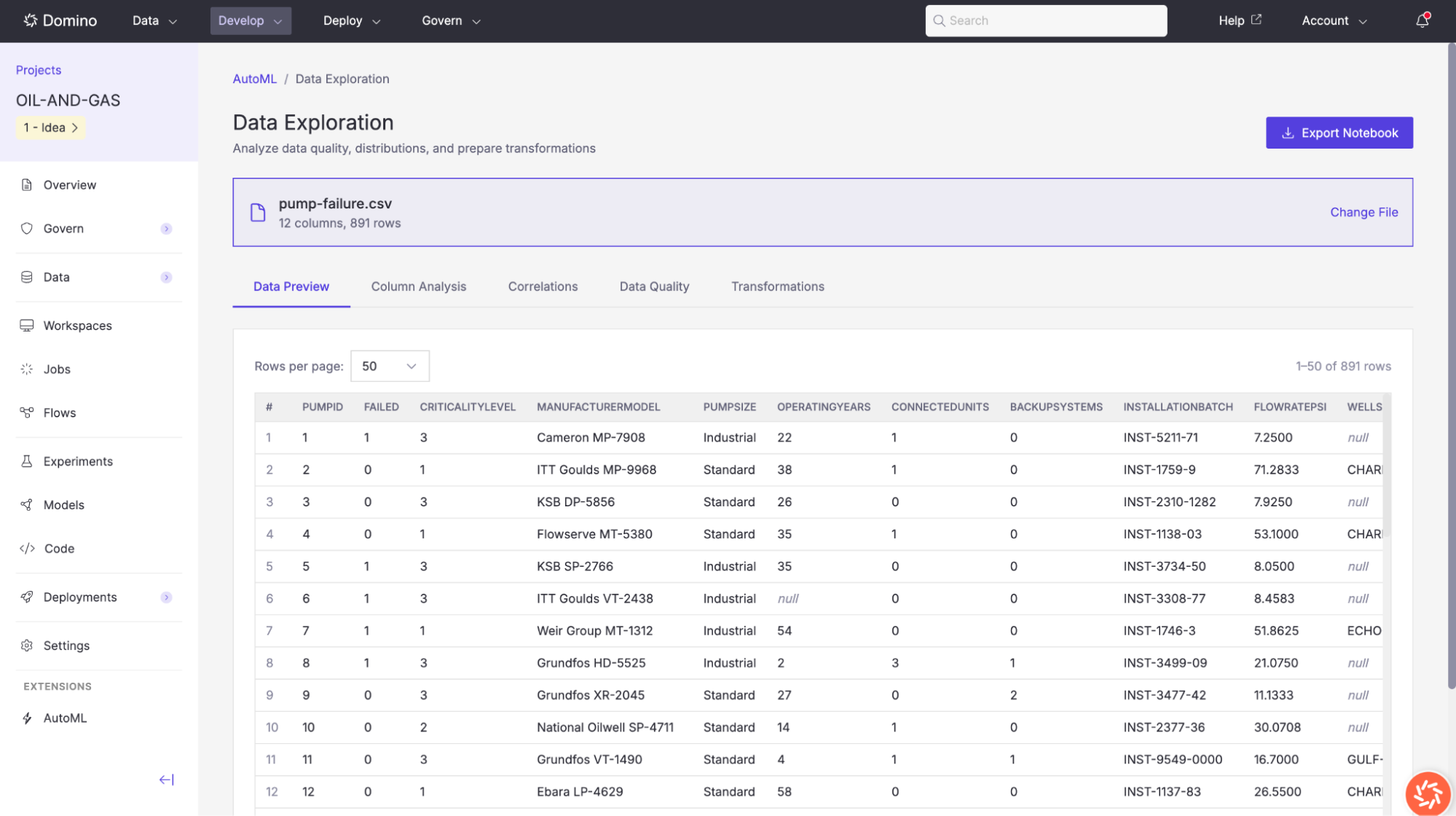
Once a file is loaded, Domino automatically profiles the data and takes you to the Data Exploration interface. The file name, column count, and row count are displayed at the top of the page. You can switch to a different file at any time by clicking Change File.
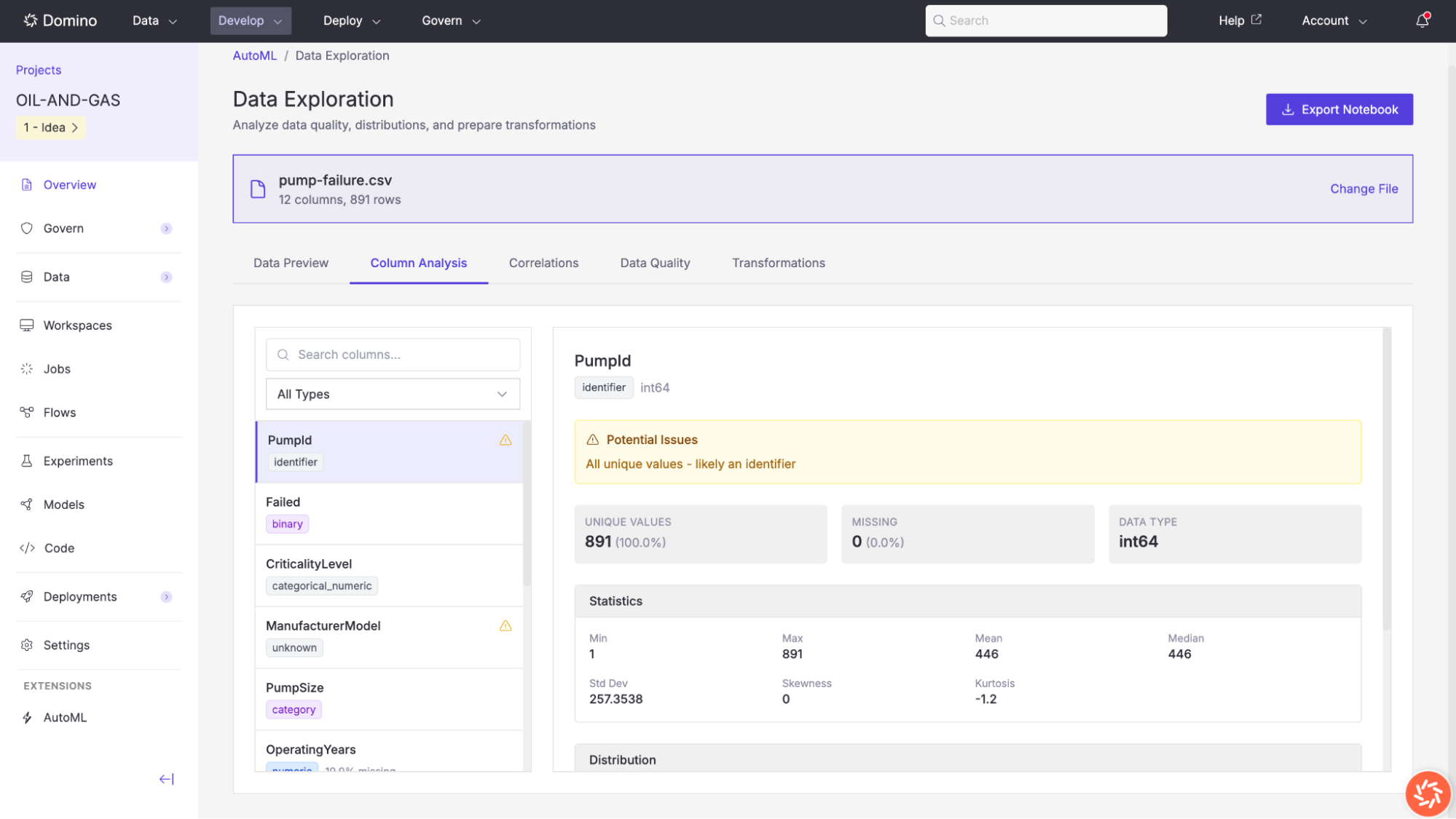
Column Analysis
The Column Analysis tab provides detailed profiling information for each column in your dataset. Select a column from the list on the left to view its profile on the right.
AutoML automatically detects each column’s semantic type, displayed as a colored tag beneath the column name. Detected types include:
| Type | Description | Color |
|---|---|---|
numeric | A column containing continuous numeric values (integers or floats). | Blue |
monetary | A numeric column identified by name patterns related to financial values (e.g., | Blue |
binary | A numeric column with exactly two distinct values, commonly used as a classification target. | Purple |
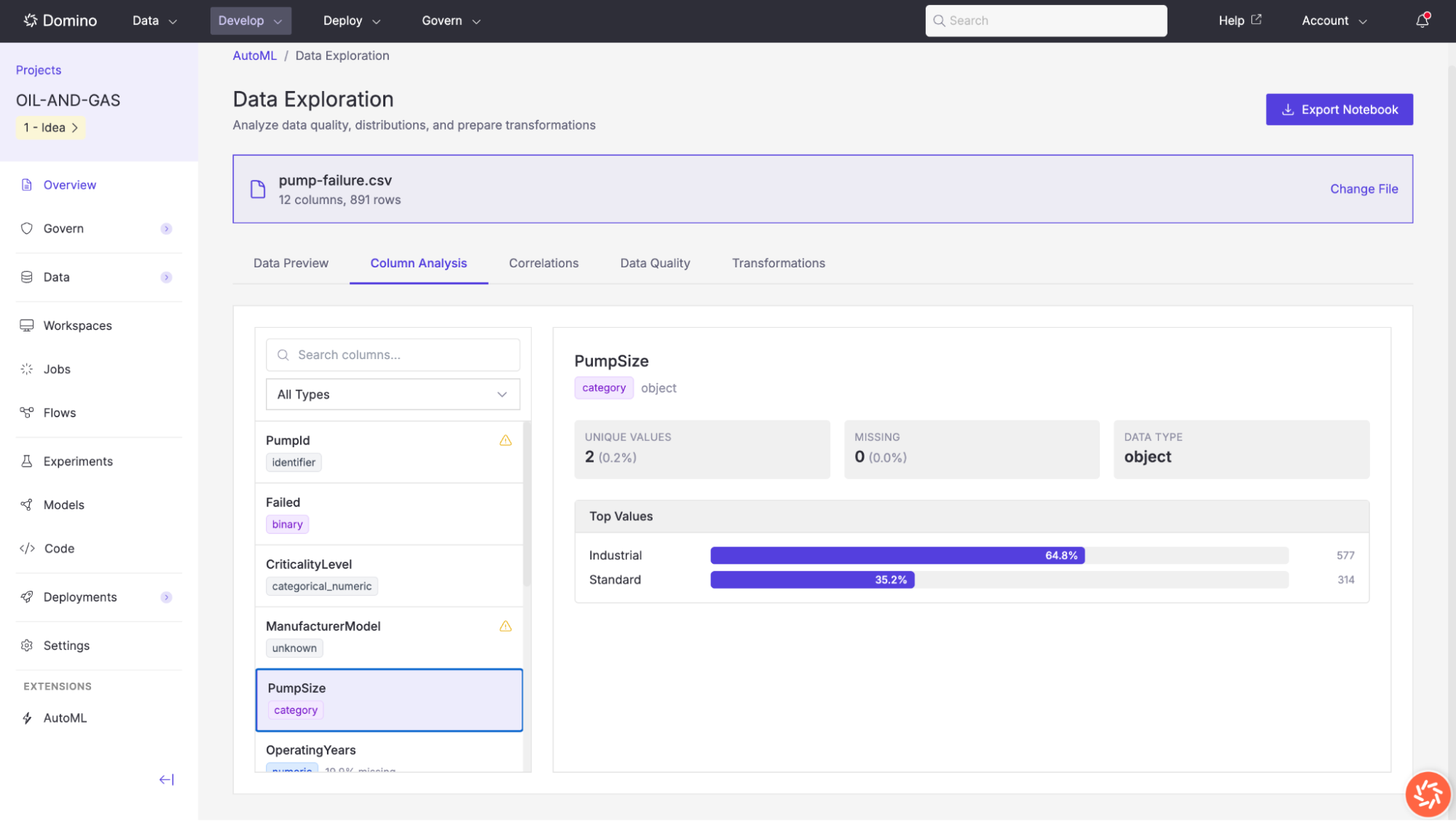
category | A column with a moderate number of distinct text or object values, or identified by name patterns (e.g., | Purple |
categorical_numeric | A numeric column with fewer than 20 distinct values representing less than 5% of the total rows, treated as a categorical feature. | Purple |
datetime | A column containing date or timestamp values, detected by data type or name patterns (e.g., | Green |
text | A column containing long text strings (average length > 100 characters), or identified by name patterns (e.g., | Orange |
identifier | A column whose values are likely unique row identifiers, detected by name patterns (e.g., | Gray |
boolean | A column containing true/false values, detected by data type or name patterns (e.g., | Gray |
unknown | A column whose type could not be confidently determined. Review these columns manually before training. | Gray |
Additional types are detected but displayed with default styling:
-
email: Columns with email-related names
-
phone: Columns with phone-related names
-
url: Columns with URL-related names
-
latitude/longitude: Geographic coordinate columns
-
percentage: Columns with percentage-related names (e.g.,
percent,pct,ratio,rate) -
name: Columns with name-related patterns (e.g.,
name,title,label) -
count: Columns with count-related names (e.g.,
count,num,qty,quantity)
For each selected column, the following information is displayed:
-
Potential Issues: Warnings such as
High cardinality – may be an identifier,High missing rate, orConstant or near-constant column. -
Unique Values: The count and percentage of distinct values.
-
Missing: The count and percentage of null or missing entries.
-
Data Type: The underlying Pandas data type (e.g.,
int64,object,float64). -
Statistics: For numeric columns:
min,max,mean,median,standard deviation,skewness, andkurtosis. -
Distribution: A histogram for numeric columns, or a bar chart of top values for categorical columns showing the count and percentage for each category.
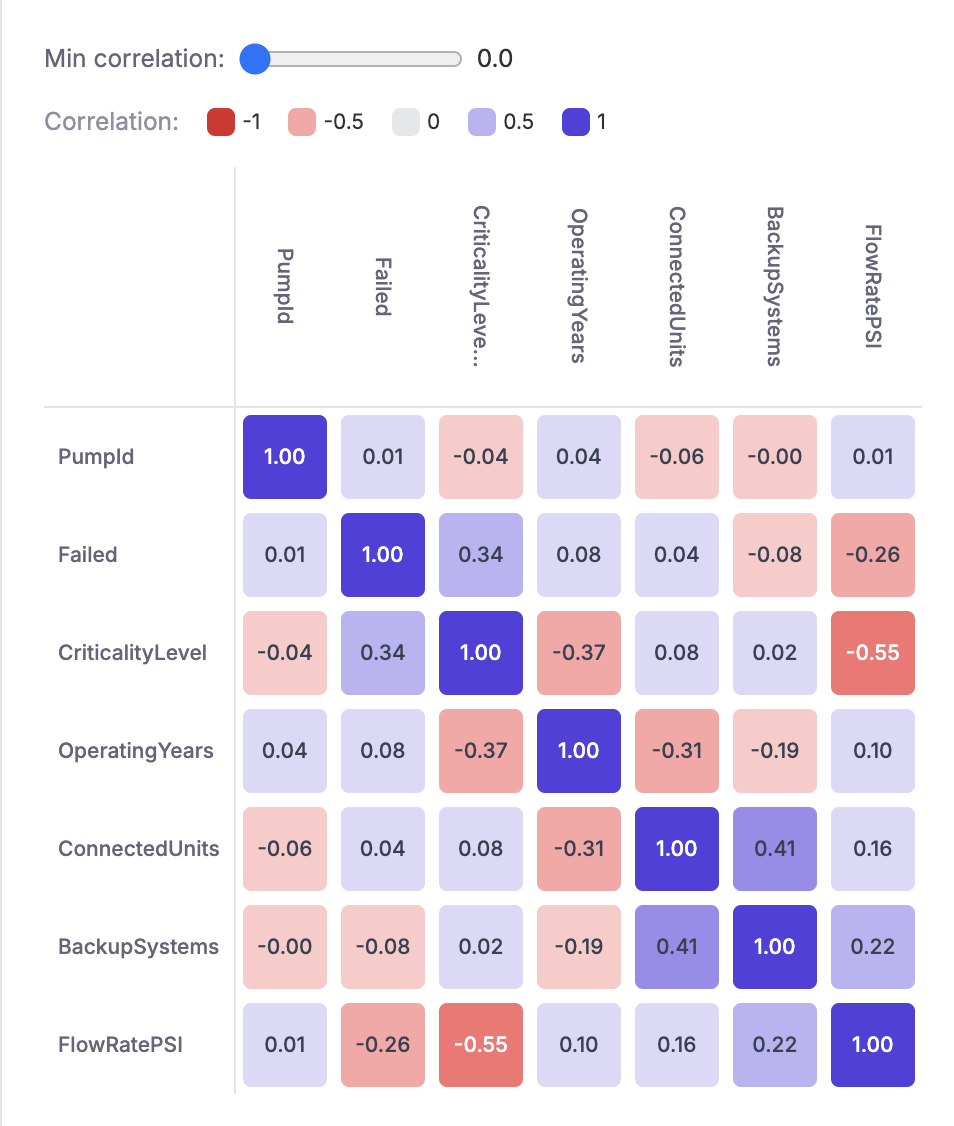
Correlations
The Correlations tab displays a correlation matrix heatmap for all numeric columns in the dataset. Correlation values range from −1 (strong negative correlation) to +1 (strong positive correlation), with color coding to highlight the strength and direction of each relationship.
Use the Min correlation slider to filter out weak correlations and focus on the strongest relationships. This view is helpful for identifying multicollinearity between features and understanding which variables are most associated with your target column.
Data Quality
The Data Quality tab gives you an at-a-glance assessment of your dataset’s readiness for model training. It includes the following sections:
-
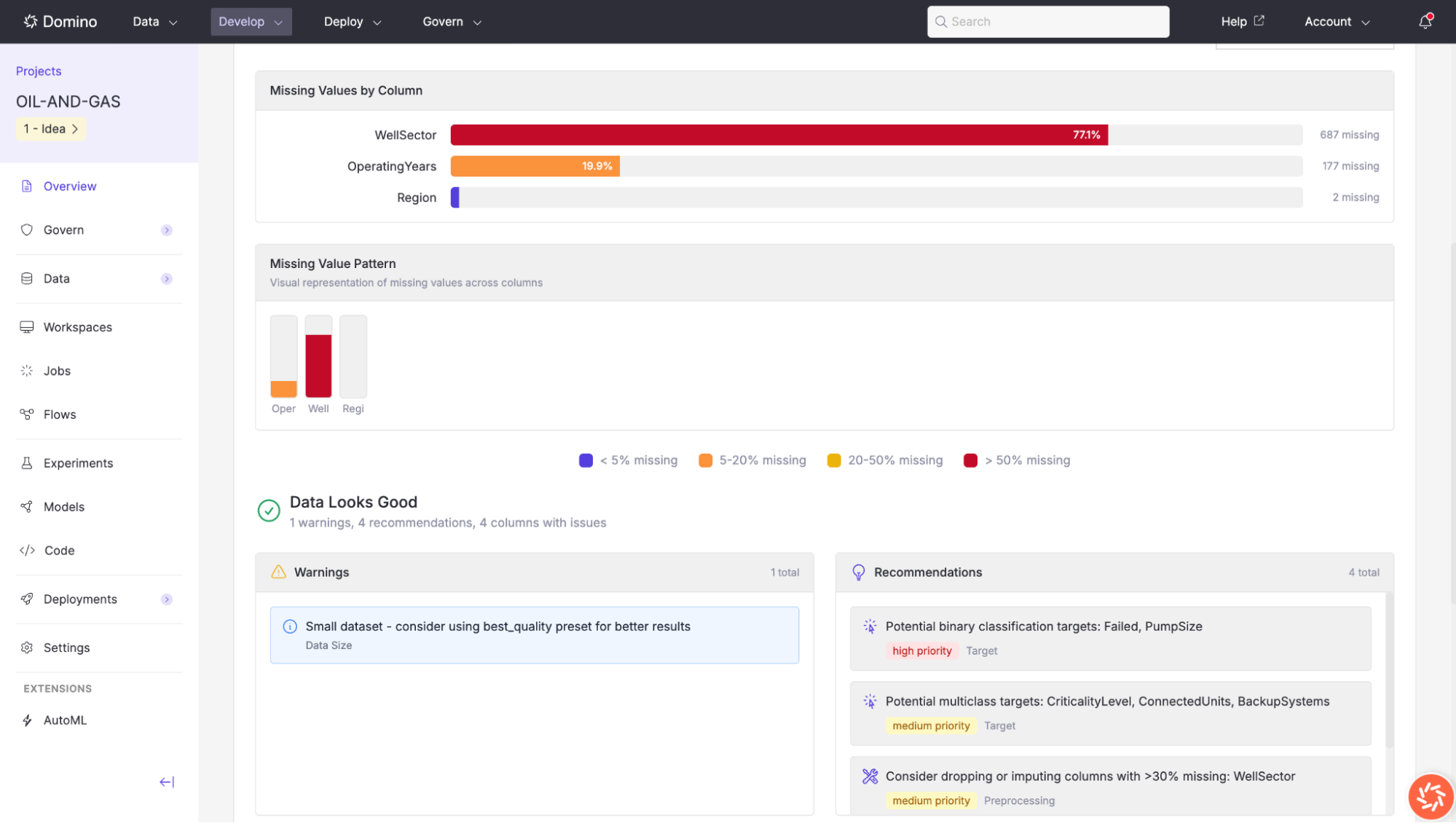
Missing Values by Column: A horizontal bar chart showing the number and percentage of missing values for each column that has any. Columns are color-coded by severity: green for less than 5% missing, orange for 5–20%, yellow for 20–50%, and red for more than 50%.
-
Missing Value Pattern: A compact visual representation of where missing values occur across columns, helping you identify whether missingness is concentrated or scattered.
-
Warnings: Issues that could affect training quality. For example,
Small dataset – consider using best_quality preset for better results. -
Recommendations: Actionable suggestions to improve model performance. These are tagged by priority (high or medium) and category (Target, Preprocessing). Examples include:
-
Potential binary classification targets (e.g.,
Failed,PumpSize). -
Potential multiclass classification targets (e.g.,
CriticalityLevel,ConnectedUnits,BackupSystems). -
Consider dropping or imputing columns with more than 30% missing values (e.g.,
WellSector).
-
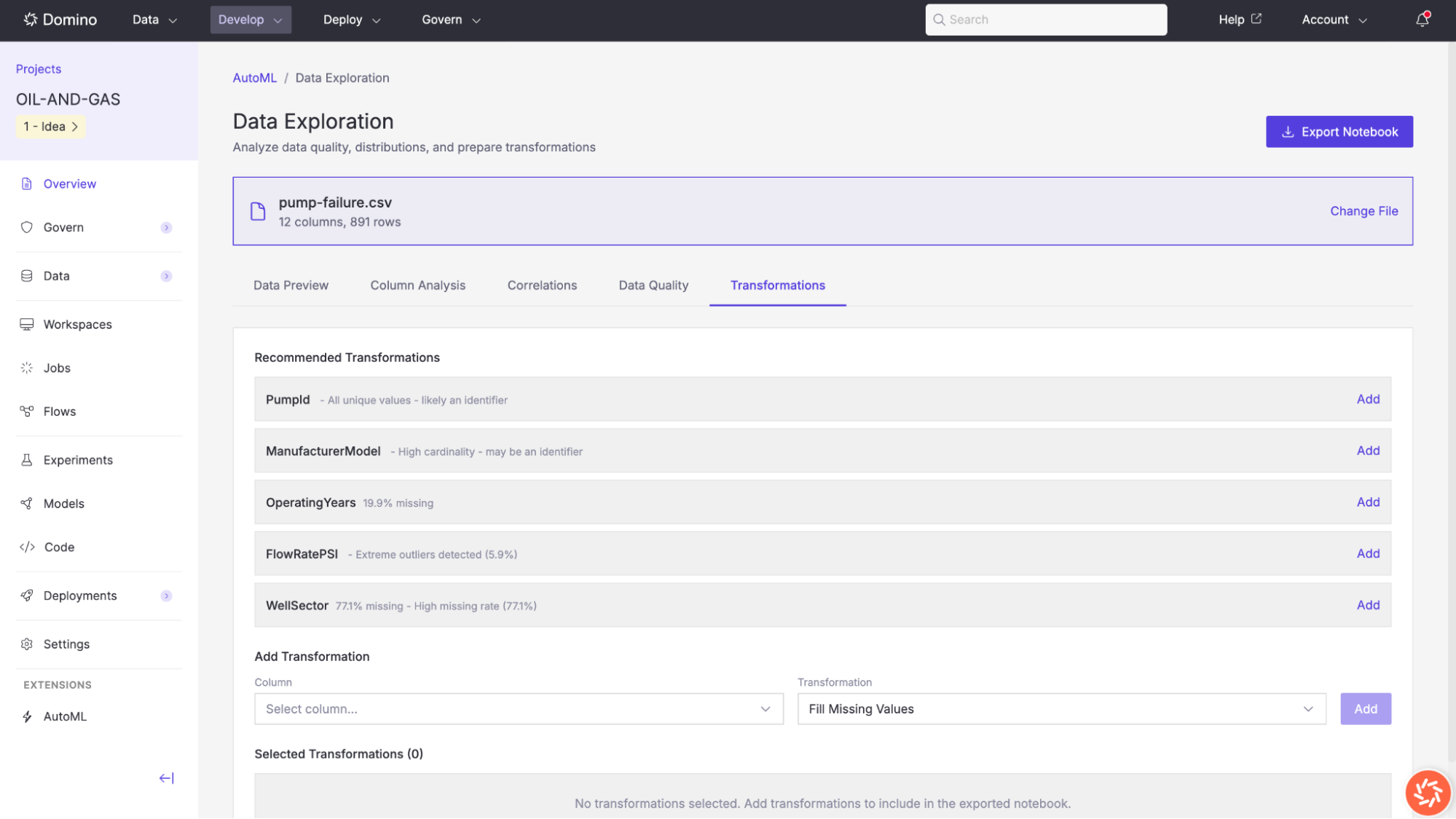
Transformations
The Transformations tab lets you define preprocessing steps that will be applied to the dataset before model training. AutoML analyzes your data and suggests recommended transformations based on detected issues.
Recommended transformations
AutoML may recommend transformations for columns with the following issues:
-
Identifier columns: Columns where all values are unique and are likely row identifiers (e.g.,
PumpId). Recommended action: drop the column. -
High cardinality: Columns that may be identifiers due to a very large number of unique values (e.g.,
ManufacturerModel). Recommended action: review and potentially drop. -
Missing values: Columns with a significant percentage of null values (e.g.,
OperatingYears at 19.9% missing). Recommended action: fill missing values. -
Extreme outliers: Numeric columns with extreme values detected (e.g.,
FlowRatePSI with 6.9% outliers). Recommended action: clip or remove outliers. -
High missing rate: Columns with a very high percentage of missing data (e.g.,
WellSector at 77% missing). Recommended action: drop the column.
Click Add next to any recommended transformation to include it. You can also create custom transformations by selecting a column and a transformation type (e.g., Fill Missing Values) from the dropdown controls at the bottom of the page.
All selected transformations appear in the Selected Transformations list. Transformations are included in the exported notebook and can be reviewed and modified in code.
Export a Notebook
At any point during data exploration, you can click the Export Notebook button in the top-right corner to download a Jupyter notebook that contains all of your data profiling results and any transformations you have selected.
This notebook can be opened in a Domino Workspace for further analysis or custom preprocessing.
AutoML model training uses AutoGluon to automatically train, tune, and rank multiple machine learning models. The training job wizard guides you through four steps: selecting your data source, choosing a model type, configuring training parameters, and reviewing your settings before launch.
To begin, click New training job from the AutoML landing page.
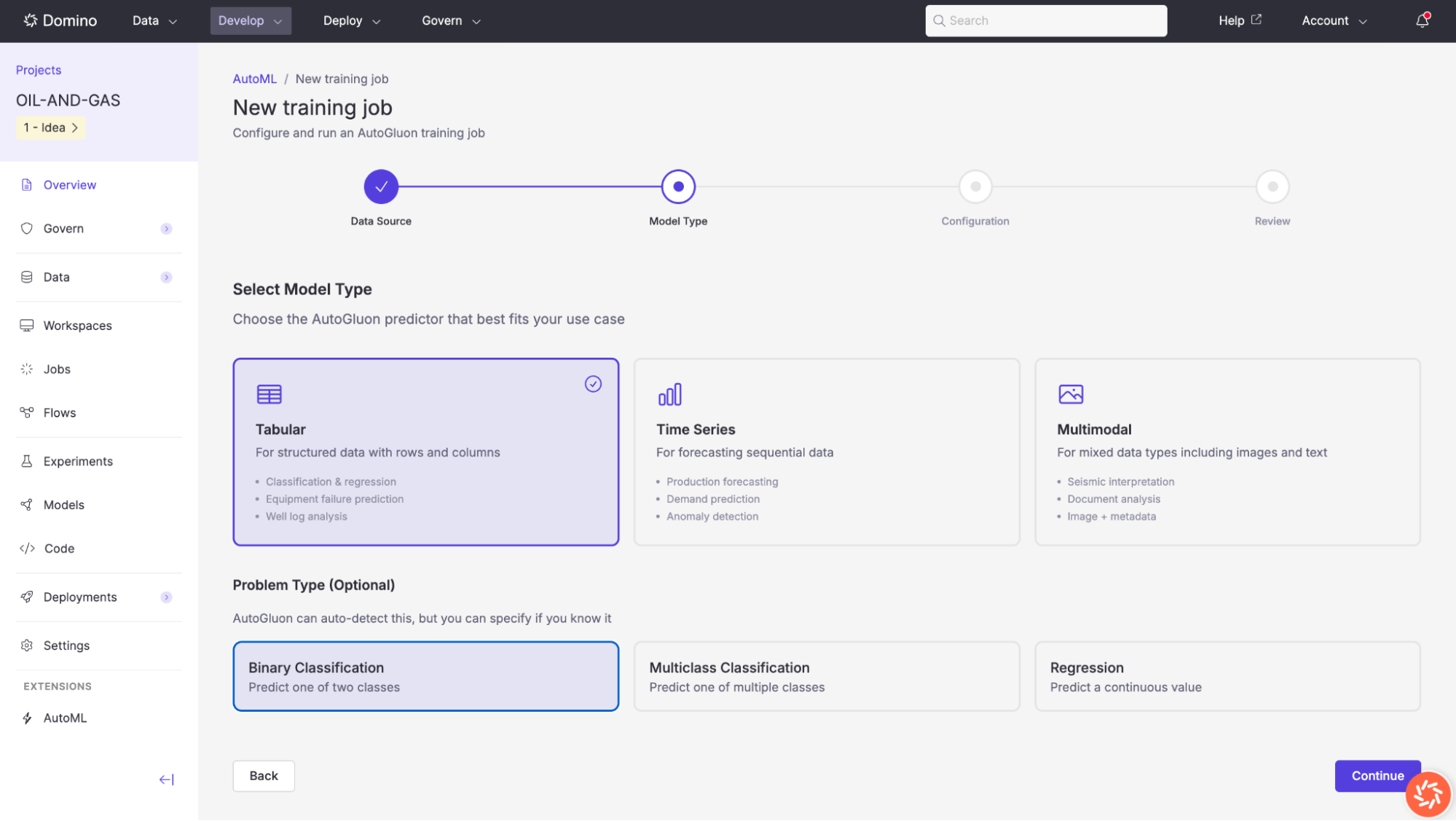
Step 2: Select a model type
Choose the AutoGluon predictor that best fits your use case. Three model types are available:
| Model type | Description | Example use cases |
|---|---|---|
Tabular | For structured data with rows and columns. Supports classification and regression tasks. | Classification and regression, equipment failure prediction, well log analysis. |
Time Series | For forecasting sequential data where observations are ordered over time. | Production forecasting, demand prediction, anomaly detection. |
Multimodal | For mixed data types that combine images, text, and tabular data. | Seismic interpretation, document analysis, image + metadata. |
Problem Type (Optional)
AutoGluon can auto-detect the problem type from your target column, but you can also specify it explicitly:
| Problem type | Description |
|---|---|
Binary Classification | Predict one of two classes (e.g., |
Multiclass Classification | Predict one of multiple classes (e.g., |
Regression | Predict a continuous value (e.g., |
Click Continue to proceed to configuration.
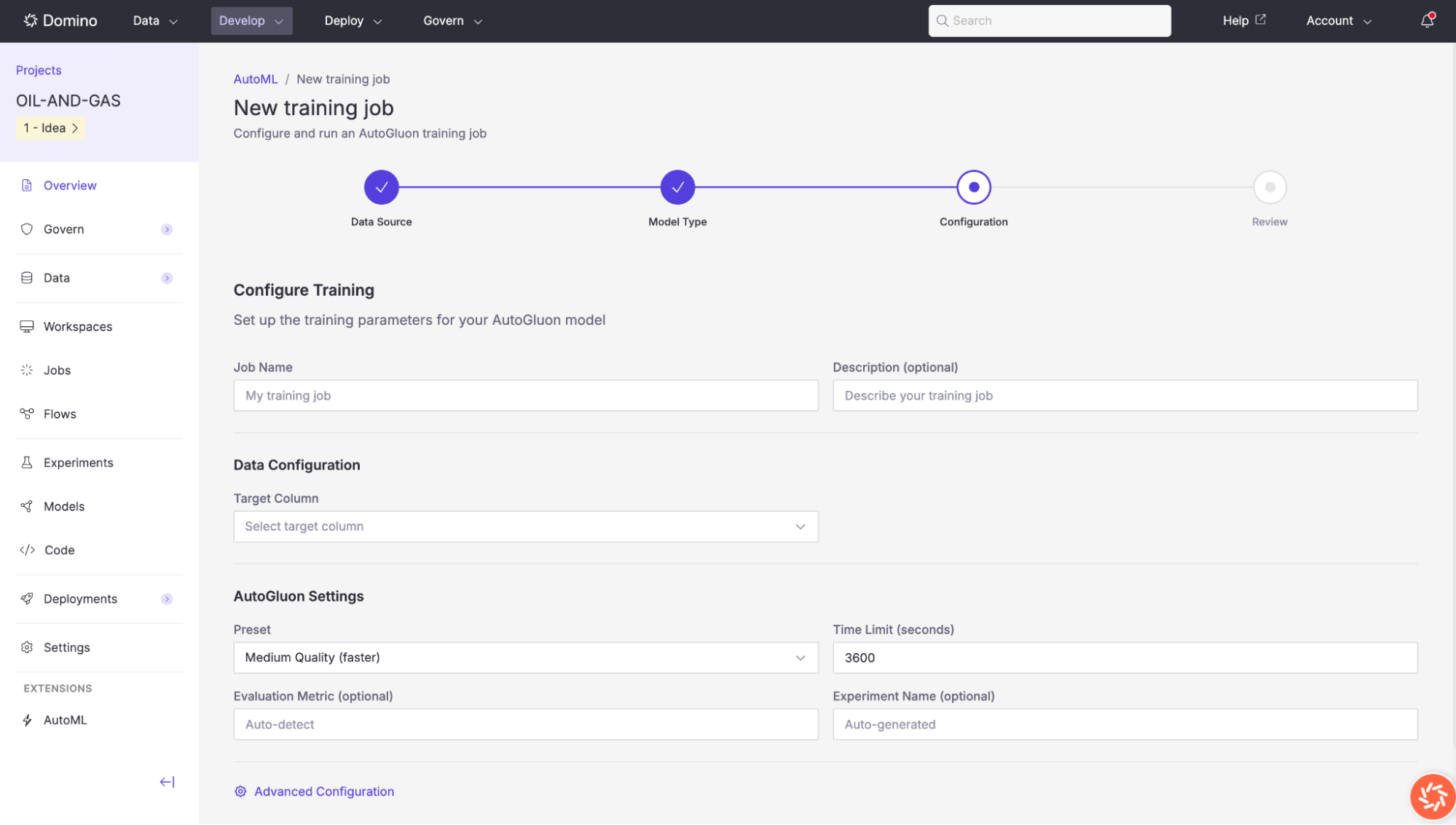
Step 3: Configure Training
The configuration step lets you define your training job’s name, target column, and AutoGluon-specific settings.
Basic configuration
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Job Name | A descriptive name for this training run (e.g., |
Description (optional) | A free-text description to help you identify this job later. |
Target Column | The column in your dataset that the model should predict. Select it from the dropdown list of available columns. |
AutoGluon settings
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Preset | Controls the trade-off between model quality and training speed. Options include |
Time Limit (seconds) | Maximum wall-clock time (in seconds) for the entire training run. Default: |
Evaluation Metric (optional) | The metric used to rank models on the leaderboard. Set to |
Experiment Name (optional) | An optional Domino Experiment name for tracking this run. If left blank, a name is auto-generated. |
Advanced Configuration
Click Advanced Configuration to access fine-grained controls organized across multiple tabs. Available tabs vary based on the selected model type.
Tabs available for all model types
Resources
Configure compute resources allocated to the training job.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Number of GPUs | Set to |
Number of CPUs | Leave empty for automatic detection based on available hardware. |
Verbosity Level | Controls logging detail: |
Cache Data | Cache data in memory for faster training. Enabled by default. |
Tabs available for tabular models only
Models
Select or exclude specific model families from the training run.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Excluded Model Types | Click to exclude model types from training (highlighted in red). Available models: LightGBM, CatBoost, XGBoost, Random Forest, Extra Trees, K-Nearest Neighbors, Linear Regression, Neural Network (PyTorch), Neural Network (FastAI). |
Bagging Folds | Number of folds for bagging (2–10). Set to |
Stack Levels | Number of stacking levels (0–3). Higher values increase ensemble complexity. |
Auto Stack | Automatically determine optimal stacking configuration. |
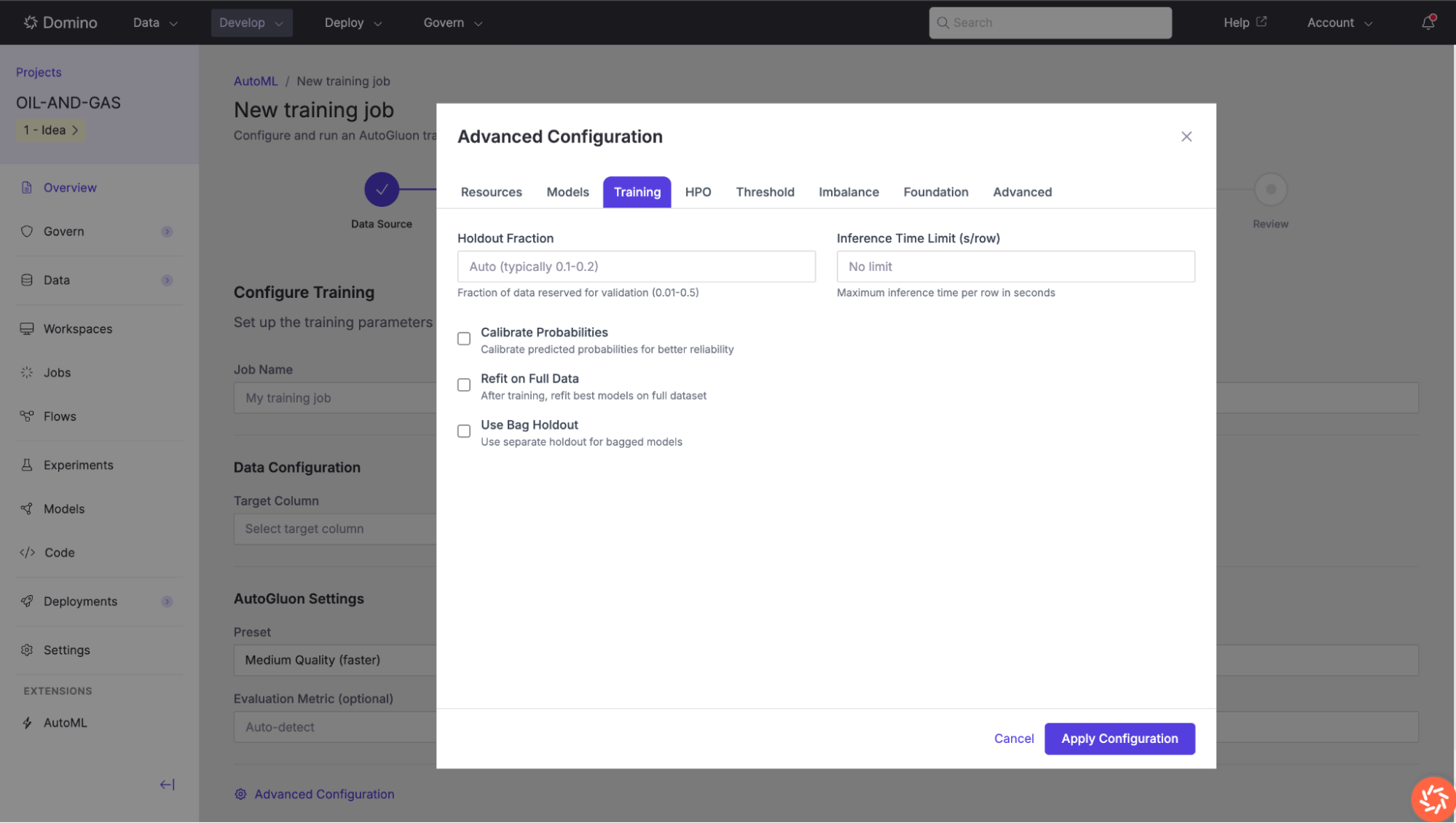
Training
Fine-tune the training process.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Holdout Fraction | Fraction of data reserved for validation (0.01–0.5). Typically 0.1–0.2. Set to |
Inference Time Limit (s/row) | Maximum inference time per row in seconds. Leave blank for no limit. |
Calibrate Probabilities | Calibrate predicted probabilities for better reliability. Useful when probability outputs will be used for decision-making. |
Refit on Full Data | After training, refit the best models on the full dataset (training + validation) for maximum performance. |
Use Bag Holdout | Use a separate holdout for bagged models, which can improve ensemble quality. |
Hyperparameter Optimization (HPO)
Enable and configure hyperparameter tuning. When enabled, AutoGluon searches over hyperparameter combinations for each model family.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Enable HPO | Toggle hyperparameter optimization on/off. |
HPO Scheduler | Local (single machine) or Ray (distributed across multiple workers). |
Search Algorithm | Auto (recommended), Random Search, Bayesian Optimization, or Grid Search. |
Number of Trials | More trials = better results but longer training (1–100). Default: |
Max Iterations per Trial | Maximum training iterations for each trial. Leave blank for auto. |
Grace Period | Minimum iterations before early stopping can occur (ASHA scheduler). |
Reduction Factor | Factor by which to reduce the number of trials at each rung. Typically |
Per-Model Hyperparameters: Override default hyperparameters for specific model types (LightGBM, XGBoost, CatBoost, Neural Network) using JSON format.
Threshold
For binary classification tasks, optimize the decision threshold.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Enable Threshold Calibration | Find optimal decision threshold instead of using the default |
Optimization Metric | Metric to optimize: |
Thresholds to Try | Number of threshold values to evaluate (10–1000). Default: |
Imbalance
Configure how AutoGluon handles class imbalance.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Imbalance Strategy | None (default), Oversample (duplicate minority class), Undersample (reduce majority class), SMOTE (synthetic minority oversampling), or Focal Loss (down-weight easy examples). |
Sample Weight Column | Name of a column containing sample weights for weighted training. |
Foundation
Options for foundation model-based approaches.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Use Tabular Foundation Models | Include |
Foundation Model Preset | None (use with other models), Zero-shot (instant predictions without training), or Zero-shot + HPO (optimize foundation model parameters). |
Dynamic Stacking | Use dynamic stacking for adaptive ensemble configurations. |
Pseudo-Labeling | Enable semi-supervised learning with unlabeled data. Requires specifying an unlabeled data path. |
Drop Unique Features | Automatically drop high-cardinality unique features (like IDs). |
Advanced
Additional low-level AutoGluon parameters for experienced users.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Enable Distillation | Transfer knowledge from the ensemble to a single faster model for deployment. |
Distillation Time Limit | Time allocated for distillation (seconds). Leave blank for auto. |
Include Only Specific Models | Whitelist specific model types to include (overrides excluded models). Selected models appear in green. |
Bagging Sets | Number of complete bagging sets (increases diversity). |
Use Refit as Best | Use the refitted model as the final predictor. |
Tabs available for time series models only
Time Series
Configure time series-specific settings.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Frequency | Data frequency: |
Target Scaler | Scaling method for target values: |
Use Chronos | Enable Amazon’s Chronos foundation model for time series forecasting. |
Chronos Model Size | Model size when Chronos is enabled: |
Enable Ensemble | Combine multiple time series models into an ensemble. Enabled by default. |
Tabs available for multimodal models only
Multimodal
Configure multimodal-specific settings for combined image, text, and tabular data.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Text Backbone | Pre-trained text model (e.g., |
Image Backbone | Pre-trained image model (e.g., |
Max Text Length | Maximum token length for text inputs (32–2048). Default: |
Image Size | Input image size in pixels (32–512). Default: |
Batch Size | Training batch size. Leave blank for auto. |
Max Epochs | Maximum training epochs. Leave blank for auto. |
Learning Rate | Model learning rate. Leave blank for auto. |
Fusion Method | How to combine modalities: |
Summary of tabs availability by model type:
| Tab | Tabular | Time Series | Multimodal |
|---|---|---|---|
Resources | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Models | ✓ | - | - |
Training | ✓ | - | - |
HPO | ✓ | - | - |
Threshold | ✓ | - | - |
Imbalance | ✓ | - | - |
Foundation | ✓ | - | - |
Advanced | ✓ | - | - |
Time Series | - | ✓ | - |
Multimodal | - | - | ✓ |
Once a training job is launched, its results page provides comprehensive information about the run’s progress and outputs.
The results page is organized into several tabs: Overview, Leaderboard, Diagnostics, Metrics, Outputs, and Logs.
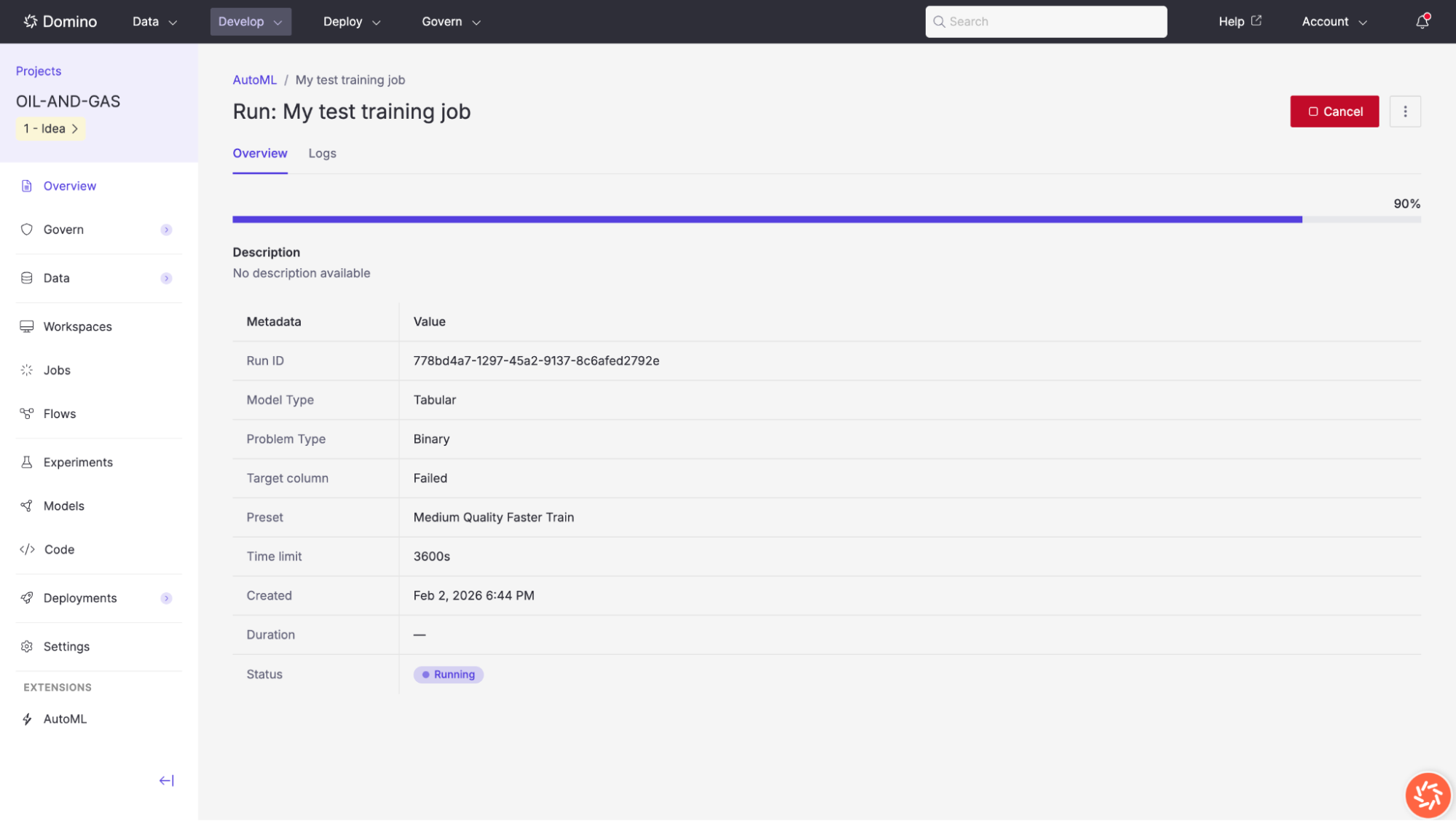
The Overview tab displays the training job’s metadata and real-time progress. While the job is running, a progress bar shows the estimated completion percentage and a Cancel button is available to stop the run.
The metadata table includes:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Run ID | A unique identifier for this training run. |
Model Type | The predictor type (e.g., |
Problem Type | The detected or specified problem type (e.g., |
Target Column | The column being predicted (e.g., |
Preset | The quality preset used (e.g., |
Time Limit | The configured time limit in seconds (e.g., |
Created | The date and time the job was launched. |
Duration | Total elapsed time for the training run. |
Status | Current status: |
After training is complete, you can deploy the best model directly from the AutoML interface.
Export a Deployment Package
-
Navigate to the Outputs tab of your completed training run.
-
Verify the output directory path under Deployment Package.
-
(Optional) Check Optimize for inference to reduce model size and improve prediction latency.
-
Click Create Package.
The generated package is saved to the specified directory in your Domino project’s dataset storage. It includes the model artifacts, inference script, requirements file, and Dockerfile.
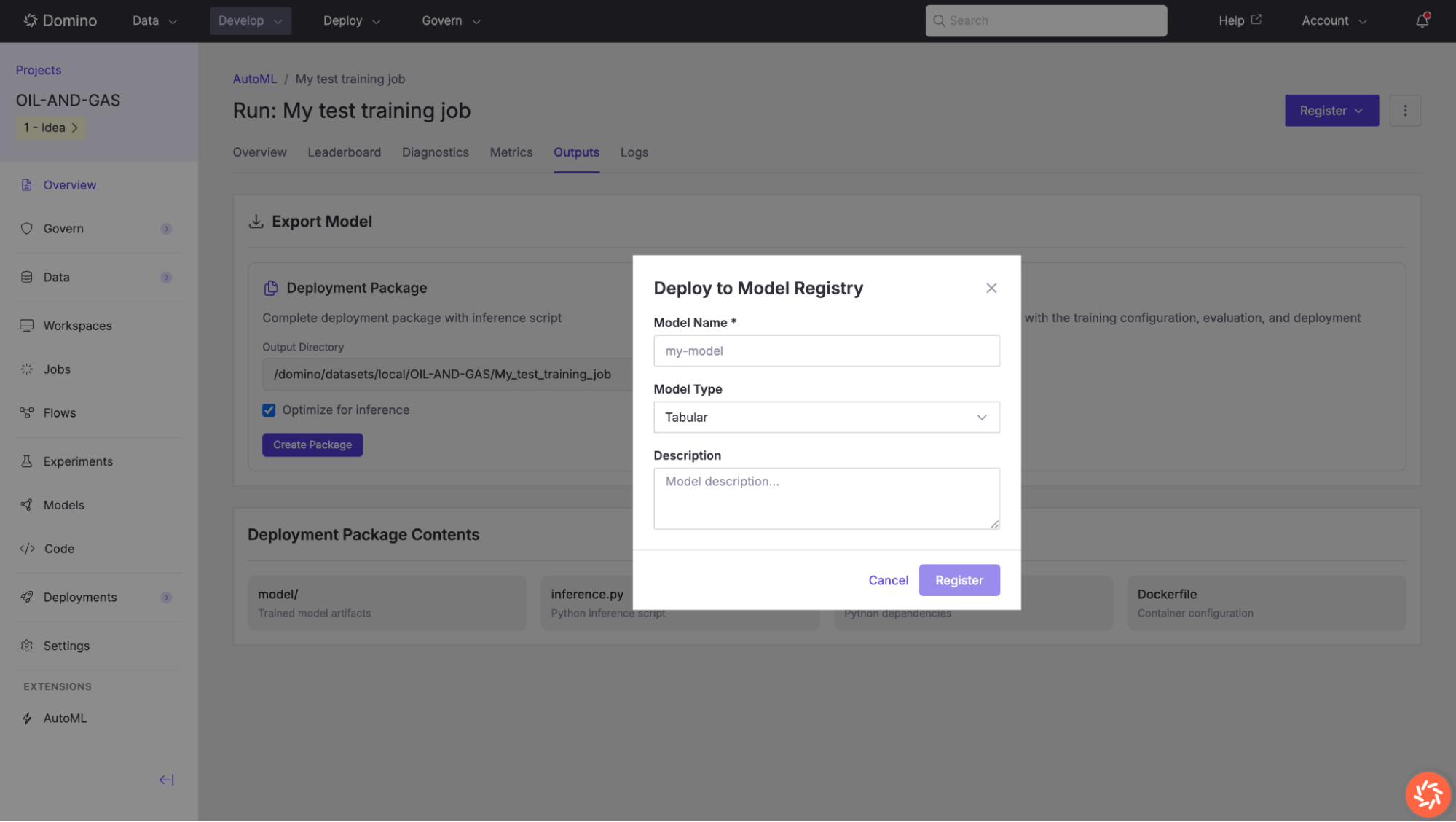
Register a Model
To register your model in Domino’s Model Registry for versioning, governance, and deployment:
-
Click the Register button in the top-right corner of the training results page.
-
In the Deploy to Model Registry dialog, enter a Model Name.
-
Select the Model Type (e.g.,
Tabular). -
Optionally add a description to document the model’s purpose and training context.
-
Click Register to save the model to the registry.
Once registered, the model appears in the Models section of your Domino project and can be deployed as an API endpoint, used in batch scoring, or shared across teams.
-
Review data quality before training. Use the Data Exploration tool to inspect missing values, outliers, and column types. Address high-priority recommendations (especially dropping or imputing columns with more than 30% missing data) before starting a training job.
-
Choose the right preset. The Medium Quality (Faster) preset is a good starting point for rapid iteration. Once you have identified a promising dataset and target, switch to Best Quality for production models, especially on smaller datasets where the additional training time yields meaningful improvements.
-
Set an appropriate time limit. A longer time limit allows AutoGluon to train more models and explore more hyperparameter configurations. For initial exploration, 600–1800 seconds is often sufficient. For production runs, consider 3600 seconds or more.
-
Exclude identifier columns. Columns with all unique values (flagged as identifiers) do not contribute meaningful signal and should be dropped before training. AutoML will flag these in both Column Analysis and Recommended Transformations.
-
Examine feature importance. After training, review the Feature Importance chart on the Diagnostics tab. If unimportant features dominate, consider removing them and retraining to reduce noise and improve generalization.
-
Consider the prediction time trade-off. Ensemble models (e.g., WeightedEnsemble_L2) typically achieve the best validation scores but may have higher inference latency. For real-time applications, compare leaderboard scores with prediction times and consider selecting a simpler model that meets your latency requirements. Use the exported notebook for reproducibility. Download the Training Notebook from the Outputs tab to preserve a complete record of your training configuration. This notebook can be re-run in a Domino Workspace and serves as the starting point for any custom modifications.