Policies define review and approval workflows for deliverables, such as models, reports, and AI systems. Use policies to codify internal risk controls, regulatory frameworks, or corporate standards across your organization.
Only Governance administrators can create, edit, or publish policies. Roles and security has details on role assignment.
You can build policies in two ways:
-
Policy Builder: A visual UI for defining policies step-by-step
-
YAML: A code-based method for advanced customization
Once published, policies enforce compliance at runtime when applied to governed bundles.
Policies can:
-
Require approvals before releasing models or reports
-
Capture evidence and risk classifications during review
-
Show or hide questions based on input
-
Define multi-stage workflows with approvers and conditions
-
Use gates to restrict specific actions, such as publishing apps or creating model endpoints, until all required approvals are complete
You can create a policy either from scratch or by using an existing template. Both methods allow you to use the Policy Builder UI or the Code editor.
Choose a view
Once created, the policy opens in the Policy Builder by default. You can switch between these views at any time:
-
Policy Builder (UI editor): Guided form for building stages, rules, and questions
-
Graph view: Visual overview of the policy’s workflow
-
Code editor: Raw YAML editor for advanced configuration
Note: If editing YAML directly, remember to replace user-organization-name with your organization’s name to correctly assign approvers.
Policies are written in YAML and must be published before use. Build governance policies in our documentation has more building blocks for advanced customization.
Use the Policy Builder
The Policy Builder is a guided interface for defining policy components without writing YAML.
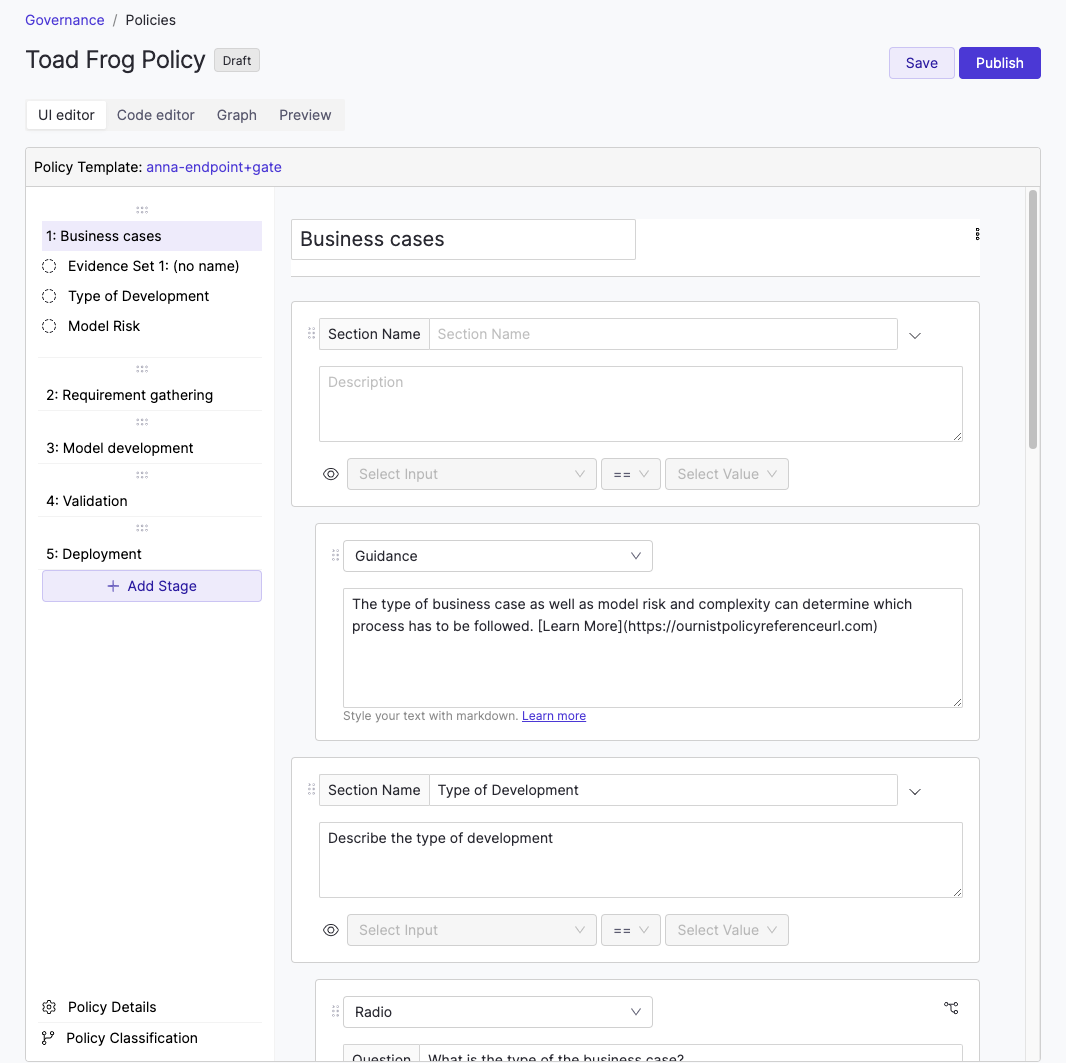
In this UI editor, you can:
-
Define policy stages such as validation or deployment
-
Assign approvers to each stage
-
Add evidence questions approvers must answer
-
Add scripted checks for model validation
-
Configure classification and visibility rules
Domino automatically generates YAML behind the scenes as you work in the builder. You can view or modify this YAML in the Code editor at any time.
You can use rules to evaluate evidence, classify policy executions, and control which sections of a policy are shown to users. Classification and visibility rules often work together. For example, a classification rule can drive a visibility rule.
Classification rules
You can use classification rules to apply tags or labels to a policy execution based on collected evidence. These outputs can:
-
Trigger downstream rules
-
Influence policy bundle matching
-
Inform audit or compliance filters
Policy components has YAML configuration details and examples for classification rules.
Visibility rules
Visibility rules can be applied to sections of a policy, such as to show or hide specific stages or questions based on earlier responses. Use the eye icon in the section header to define a visibility condition.
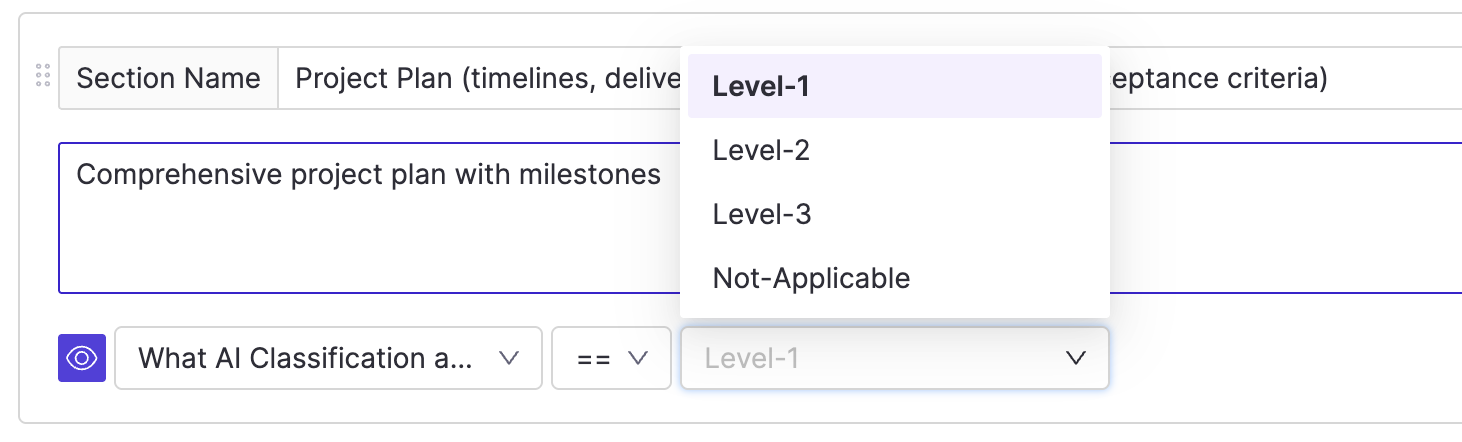
To configure a rule:
-
Choose the input question to evaluate
-
Specify the value that must be selected to make the section visible
Use a custom visibility rule if you need to:
-
Reference more than one input question
-
Use classification values to control visibility
Custom visibility rules can reference the output of a classification rule. This allows you to show or hide sections based on computed logic, not just raw inputs.
Policy components has YAML configuration details and examples for visibility rules.
Gating controls when certain operations are allowed based on policy status. For example, you can block a user from publishing an app until all stages in the associated policy bundle are approved.
Gates must be defined in YAML. Gates has details about how gates work and how to define them.
You can modify a published policy by creating a new version. The new version remains in draft until it is published.
When publishing the new version, you can:
-
Choose whether the update is mandatory or optional for bundles using an earlier version
-
Select which bundles will be affected
-
Decide whether to retain or revoke existing approvals
Domino displays a list of bundles using the current version. If you mark the update as mandatory, you must select which bundles it applies to. Those bundles will be marked out of compliance until upgraded.
You can choose whether to retain or revoke existing approvals. Only revoke existing approvals if the new version includes significant or breaking changes.
You can archive policies to reduce clutter in the policy table. Archived policies:
-
Cannot be restored
-
Do not link to a detail page
-
Only appear when the Archived filter is applied
To archive a policy:
-
Go to Govern > Policies and find the policy to archive.
-
Click the … menu next to the policy and select Archive.
-
If no active bundles use the policy, click Confirm.
-
If active bundles are using the policy, Domino shows a warning and prevents archival.
-
Policy components: YAML configuration details for policies
-
Create bundles: package models and artifacts for review
-
Gates: control governed actions based on approval status
-
Glossary of Governance terms: key concepts used throughout Governance
