Domino Workspaces function as a server. You can use your preferred tools in a reproducible and customizable Environment.
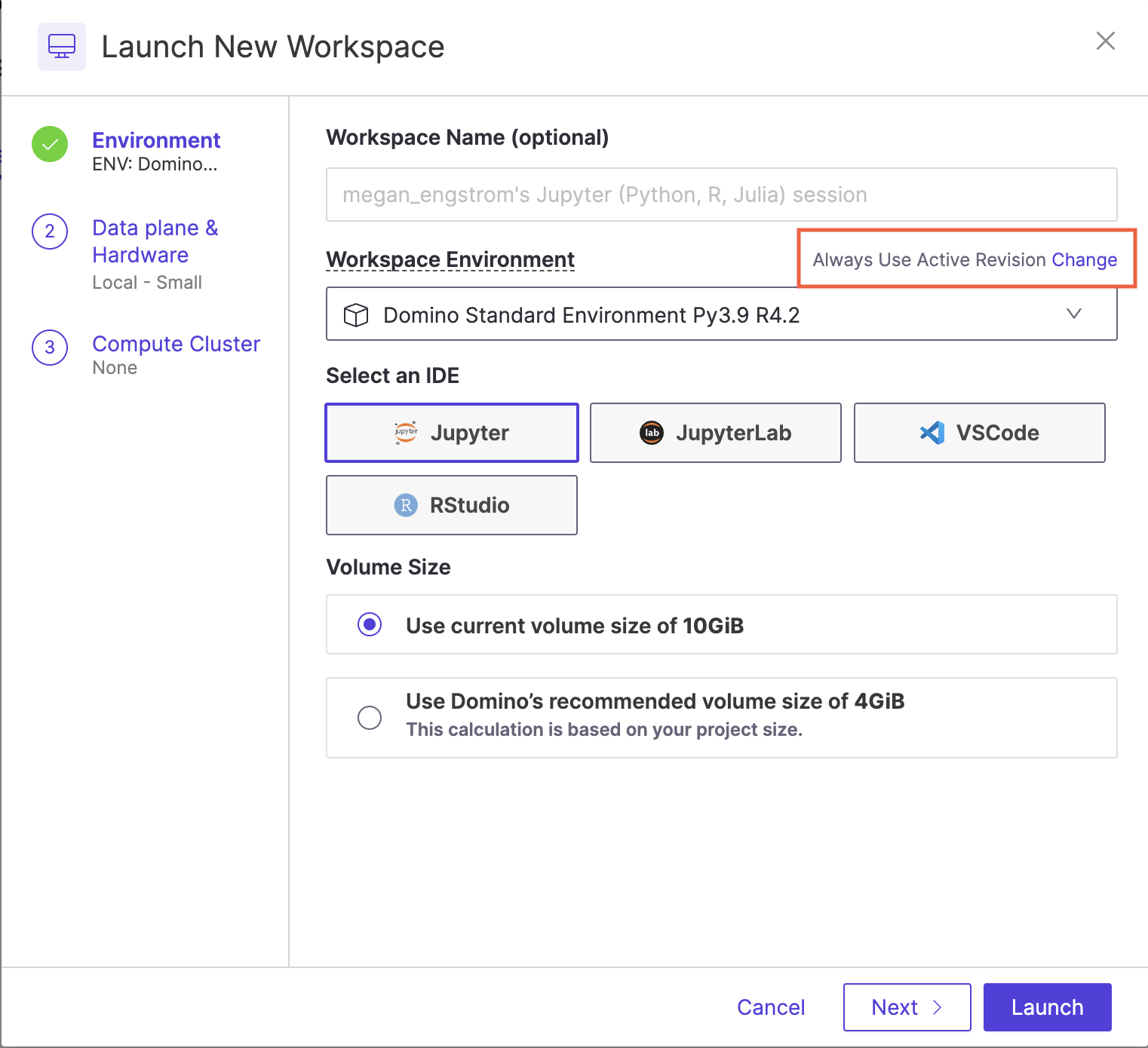
Select an Environment for your Workspace.
You can click one of Domino’s pre-defined Environments, or create a custom Environment. See Customize Environments to learn more about managing Environments.
By default, Domino uses the latest revision of your Environment. To use another revision of the Environment:
-
In the Workspace Environments section, click Change to see the revisions for the Environment.
-
Click the revision of the Environment you want for your Workspace. The version you selected displays in the Revision field.
If you see the Not Recommended warning, then Domino recommends using the active revision set by the Project owner.
|
Note
| Restricted Projects may limit your choice of Environments. |
Select the integrated development environment (IDE) that you’ll use in your Workspace (such as Jupyter).
The selected Environment determines the available IDEs.
See Add Workspace IDEs to learn how to manage IDEs.
If your administrator has enabled volume provisioning recommendations, you can select a Volume Size recommended by Domino based on your Project size and previous usage, instead of the default volume size.
|
Note
| In a Git-based Project, the first Workspace you launch always uses the volume size configured in your Project settings. Subsequent Workspace launches receive volume provisioning recommendations. |
Click next and select a Hardware tier.
A hardware tier represents the compute hardware — CPU, memory, and other resources like GPUs — used for your Run. It can be a virtual instance in a cloud services provider, or a physical machine running in your deployment’s on-premise data center. Workspace scheduling requires a server with adequate free resources; otherwise, the Workspace queues until resources free up or a new server is available. Selecting a smaller hardware tier can speed up provisioning. Opt for the smallest tier that fulfills your task’s needs.
In a hybrid deployment, hardware tiers in the dropdown are grouped by data plane, such as GCP europe-central2 below.
The Local data plane corresponds to running the Workspace in the Domino control plane cluster.
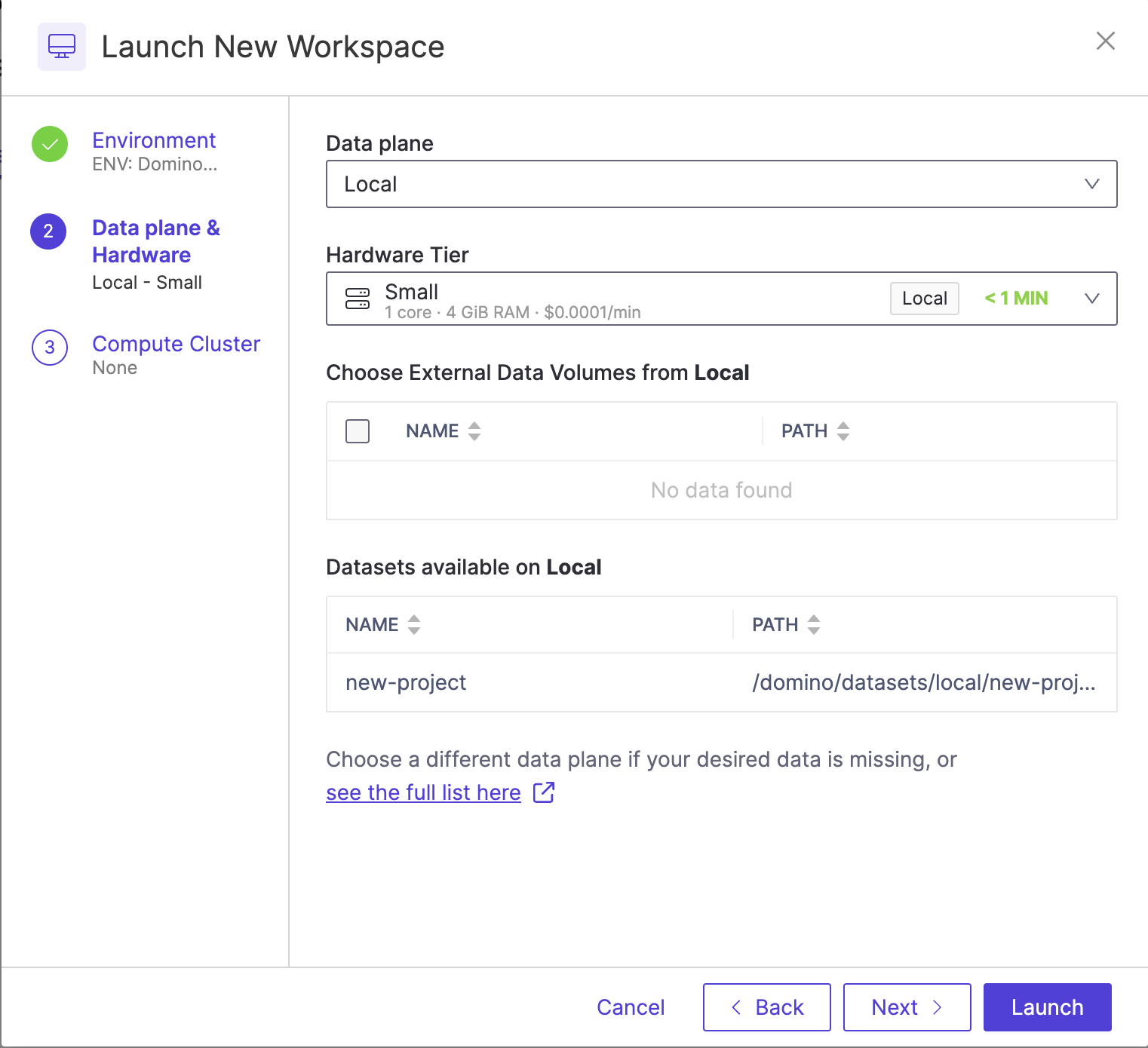
Mount data
Domino shows you what data is available to be mounted to your Workspace, based on the selected data plane.
To ensure faster startup times, only select the data that you need.
|
Tip
|
|
-
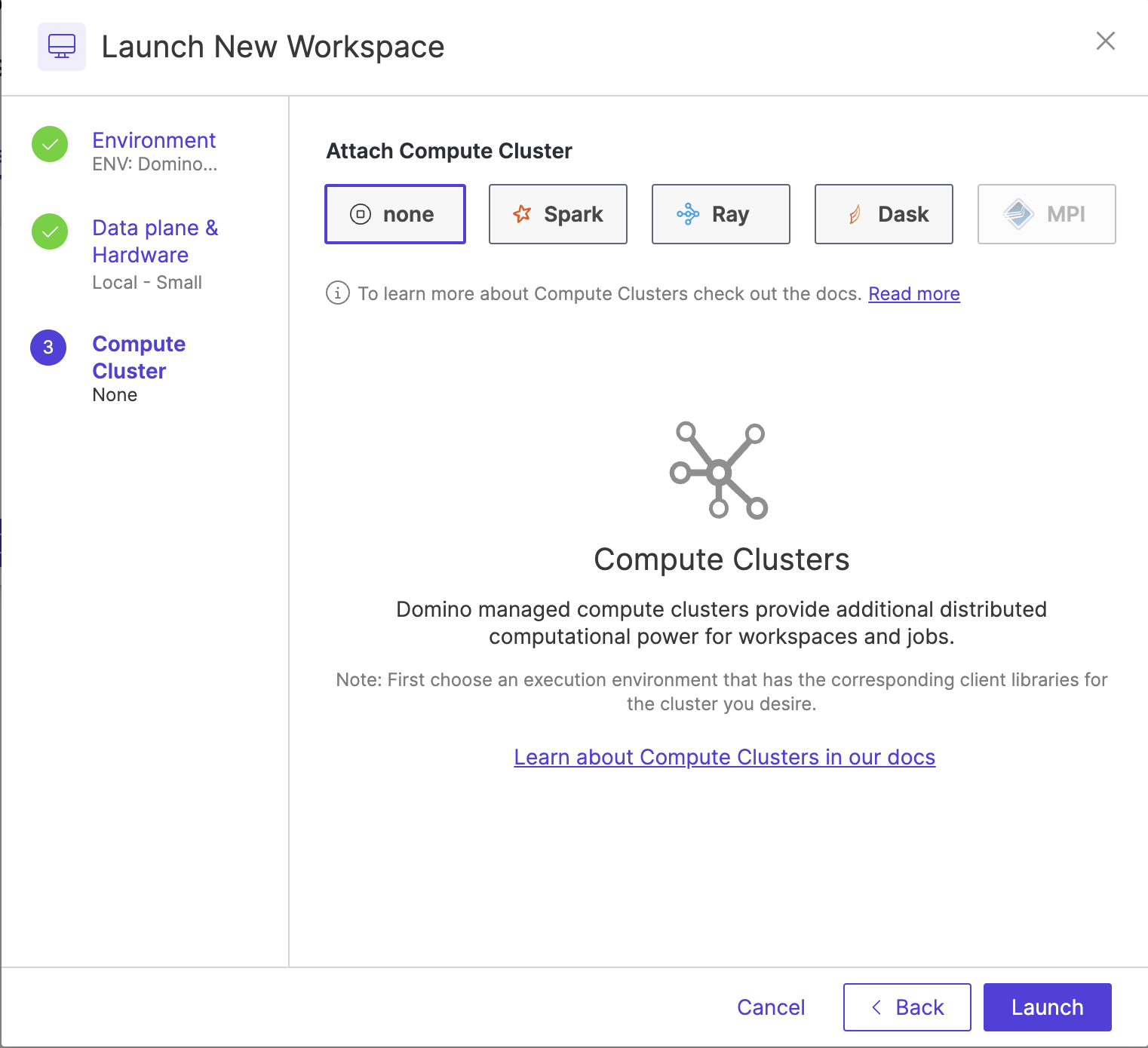
Click Next to attach a compute cluster or view additional details of the Workspace (or click Launch to skip those options).
-
If necessary, attach a compute cluster to your Workspace. To learn more about clusters, see the following:
-
Click Launch.
-
A new tab opens and the Workspace starts loading.
|
Important
|
|